The stream of biology which deals with fungi; in other words, the study about fungi is called Mycology.
- Myco=Fungi
- Logos= knowledge
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- They cannot synthesize their own food due to a lack of chlorophyll, so some of them are often found with association with algae for food. One of the best examples of such a fungi-algae combination is Lichane.
- Generally, fungi choose humid areas as their habitat.
BENEFICIAL ROLE:
Fungi are saprotrophs; i.e. collect nutrition from dead organisms. For that reason, fungi are also called decomposers; the decomposition process means the release of simple elements from organic compounds and again returns to the environment. ( ex: Fungi usually do this job after the death of both plant and animal; if fungi were absent in the world, every place might become covered by dead bodies!
- Fungi produce an amylase enzyme; this amylase can break down starch into glucose; therefore it helps to digest starch. Due to this property, amylase has an important role in the cloth industry.
- Several antibiotics are produced by fungi; one of the most important of them is penicillin; the producer organism is Penicillium notatum. Antibiotics are those chemical compounds which either inhibit the growth of microbes or totally destroy them. Doctors prescribe antibiotics to control bacterial disease; if antibiotics treatment does not continue, the disease may reach up to life-threatening stage.
- Fungi also serve plants by playing the role of Mycorrihzae. Mycorrihzae are nothing but the association of fungi with plant roots, they are long thread-like structures, these structures help plant roots to absorb water and mineral from the soil by extending themselves.
HARMFUL ROLE:
Fungi usually can digest some unusual compounds which are difficult to digest by other microbes. Keratin is one of them; it is a protein in nature and basically present in the nail, hair, and horn of animal including humans. In the case of humans, most of the nail and hair infections are caused by fungi due to the mentioned property.
They are responsible for different types of food spoilage. Types of food, their nature of spoilage and the causative agent for spoilage are represented here in tabular form:
| Types of food | Nature of spoilage | Causative agent |
| Grain (wheat, barley, cereal, rye) | Spoiled by toxins, Aflatoxin, and ergot toxin. | Aspergillus flavus produces aflatoxin, and Claviceps purpurea produces ergot toxin, which specifically spoils rye. |
| Bread, Fruit, vegetable | Soft rot, white colour powdery growth, appearance of spores in food materials | Rhizopus spp Erwinia Penicillium spp. |
| Meat, Fish | The appearance of spores in food materials, decoloration | Penicillium spp. Cladosporium spp. |
When any cattle animal ingests ergot-infected rye, this ergot toxin causes abortion of them. In the case of humans, aflatoxin causes hallucinations, tremors, and convulsions, ultimately severe damage to the central nervous system occurs.
Fungi can degrade oil and several complex dyes; this property is responsible for the damage to oil painting. Ex: AJANTA ELORA oil painting.
CULTIVATION OF FUNGI IN THE LABORATORY:
It is an easy, less time-consuming process. We get results within 1 week.
Procedure:
A. Sample collection: First of all, any fungal-infected material should be collected. Easily available are; spotted, carl leaf, spoiled vegetables, rotten fruit (lemon), pieces of bread, etc.
B. Sample processing: If the sample is leaf, then it should be washed repeatedly by normal water and distilled water respectively. This process should be repeated 3-4 times. After that, NaCl or NaOCl solution should apply upon it, and the leaf sample should be dipped into it for 5-10 mins. This process is called surface sterilization. Then it may be cut into pieces or remain intact.
If the samples are pieces of bread, rotten fruit (lemon), etc. then one suspension should be created by the addition of distilled water with sample.
C. Inoculation of sample: In simple words, inoculation means samples are given into the media. Media is nothing but the nutritional support of microbes. Every media contains some basic requirements; like carbon source, nitrogen source, salt, different metal source etc.
Media preparation is also an easy process. The process is given below in tabular format:
- Media Name: Potato Dextrose Agar(PDA)
- COMPOSITION: (gm/L) Potato: 300 gm
- Dextrose: 2gm
- Agar: 20 gm
- Distilled water: 1L
At first, potatoes are boiled and then smashed. After that, distilled water is mixed with smashed potatoes and makes the total volume of suspension up to 1L. Then two remaining ingredients are mixed with this suspension. Now the media is ready to use before use it should be sterilized to remove all types of microbes including any spores.
After sterilization, media is poured into Petri plates (glass plates usually 100mm diameter) to become solidified. After solidification, the sample is inoculated.
D. Incubation: After inoculation, samples are incubated for 48 hrs. At 28 degrees centigrade temperature. After 48 hrs incubation, powdery growth of fungi occurs; spores are not developed usually at 48 hrs. Spores development requires at least one-week of incubation.
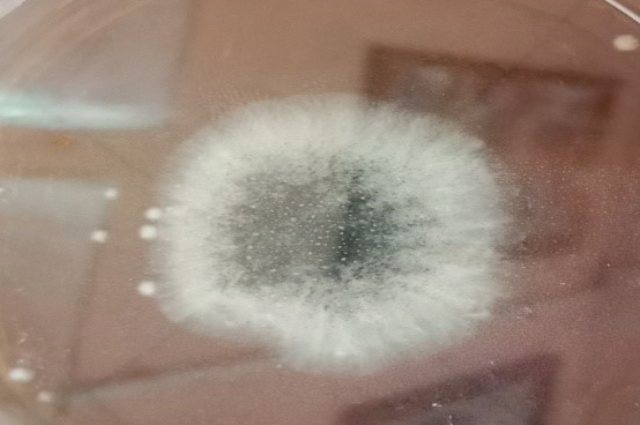

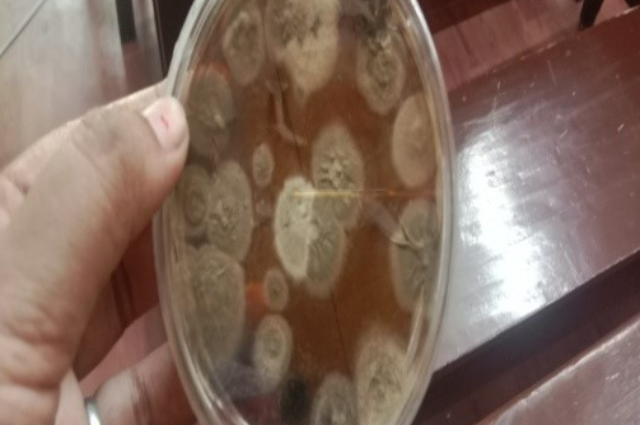
It has been reported that some spices of Penicillium produce green, blue coloured spores. They are more pathogenic than black-coloured spore-producing fungi.
Note: Both photos are captured by me during an experiment in the Laboratory.
Treatment:
Treatment of fungal disease by antibiotic is often troublesome as fungi are eukaryotic too like a human and any other animal. The side effects of antibiotics are hazardous to us. Since some azole derivatives like; Ketoconazole, Clotrimazole, Fluconazole, Albendazole, etc. are considered as effective antifungal drugs.
Finally, some important things should be kept in mind that:
- Fungi are mainly opportunistic pathogens (cause disease when immunity power is low); so we should not give the opportunity to them to harm us. To prevent fungal attacks we may take some precautions like:
- We should avoid highly humid areas (any muddy place); high moisture content allows fungal growth.
- We should avoid the scraping of normal portions of spoiled food.
- We should always discard the food material infected by fungal spores.
