General Characteristics of Pseudomonas SPP:
- Gram character: Gram-negative( Remarkable staining procedure invented by the Scientist Christian Gram; microbes who retain the red colour of safranin reagent after staining are called Gram-negative Bacteria)
- Morphology: Rod-shaped
- Motility: Unipolar motility(only one end of the cell is covered by flagella)
Family: Pseudomonadaceae
Two well-known species of this family:
i. Pseudomonas putida
ii. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Pathogenic Nature:
1. Pseudomonas spp generally causes disease, especially in an immunocompromised person, but not in healthy individuals. For that reason, they are called opportunistic pathogens.
Now, the question arises; what does it mean by the word "Immunocompromised person”?
The simple answer is those individuals which have low immunity power; i.e. susceptible to any disease rather than healthy persons. This incident occurs mainly due to three reasons:
- Long-term antibiotic treatment diminishes the normal microbial flora(NMF) which provides normal immunity power.
- Surgery itself acts as a risk factor for immunity.
- During burning, the epidermis layer of skin becomes destroyed which acts as the first line of defence. As a result, the occurrence of chance increases for secondary infection.
2. Pseudomonas spp is the causative agent of Nosocomial infection (patient-acquired infection when administered into the hospital)
Example: During catheterization (patients suffering urination problems) patients may be affected by Pseudomonas spp.
3. Its facultative aerobic nature (ability to grow under total anaerobic condition) allow them to survive in Cystic fibrosis patient (cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease where lungs and pancreas of affected individual secrete thick mucus which limits oxygen availability)
Main feature of Pseudomonas spp. is pigment production. This feature allows them to reside on the leaf of a plant because sunlight can penetrate that site at its highest and sunlight is essential for pigment production. Several pigments are produced; like:
- Pyocyanin: Blue coloured, non-fluorescent, water and chloroform soluble pigment.
- Pyoverdin: Yellowish, water-soluble, fluorescent pigment. This pigment acts as a biomarker for the detection of these microbes in food products.
Another two are Pyomelanin (brown black coloured) and Pyorubin (red coloured).
3 types of media are regularly used to grow Pseudomonas spp. in Laboratory. They are:
- Pseudomonas Isolating Agar
- Pseudomonas Agar P
- Pseudomonas Agar F
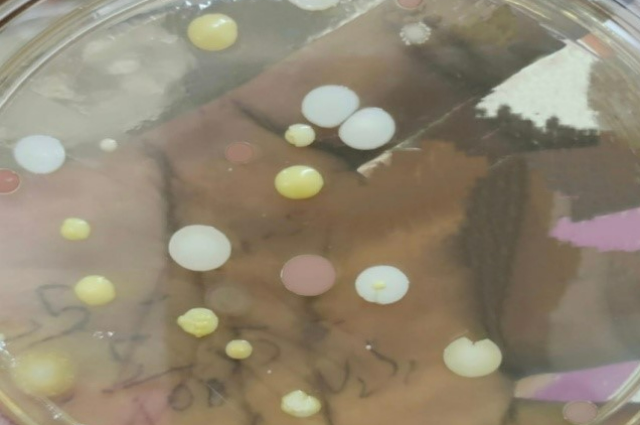
Fig: Yellow colour pigment(pyoverdin) produced by Pseudomonas spp, these pigments are water-soluble.
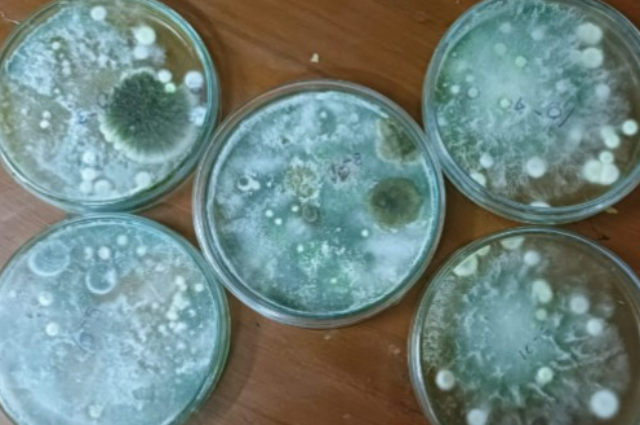
Fig: Those are fungal colonies unlike Pseudomonas spp, those pigments are water-insoluble, but soluble in organic solvents (chloroform, acetone, alcohol). This photo is also captured by me after solubility test performance in laboratory.
All 3 media contains two essential components; MgCl2 and KSO4; both promote pigment production; especially Pyocyanin.
- Pseudomonas Agar P contains glycerol which is an energy source and also promotes Pyocyanin production.
- In addition, Pseudomonas Isolating Agar contains Irgasan antibiotics which selectively inhibit Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria other than Pseudomonas spp.
- One unique feature of Pseudomonas spp is the ability to use Xenobiotics as a growth substance; Xenobiotics are those compounds which naturally do not belong to the living system; they are exclusively produced artificially by human activities.
By this property, Pseudomonas spp can detect explosive compounds such as landmines present in the soil. TNT is a major component of landmines. Therefore, if any soil sample contains Pseudomonas spp.; there is a high chance that the particular soil sample also contains TNT-like explosive!!
