Photo by zhang kaiyv on Unsplash
Water is the prerequisite element of all forms of life. Without water, the flow of life will be ceased.
A study about water ecosystems is called Lymnology.
Sources of water are collectively called waterbodies; i.e. springs, lakes, ponds, rivers, etc. Those water bodies contain both fresh and contaminated water:
- Freshwater: It is also called pure water; because it is colourless, tasteless as well as odorless. If any property out of three is present, that type of water should not be considered pure/fresh water.
On the other hand, if the water contains an obnoxious smell, unpleasant taste and turbid appearance instead of transparency, that type of water should be considered as contaminated/polluted water.
Now, a clear structural scenario of freshwater bodies should be discussed. The ideal examples of freshwater bodies are rivers and lakes.
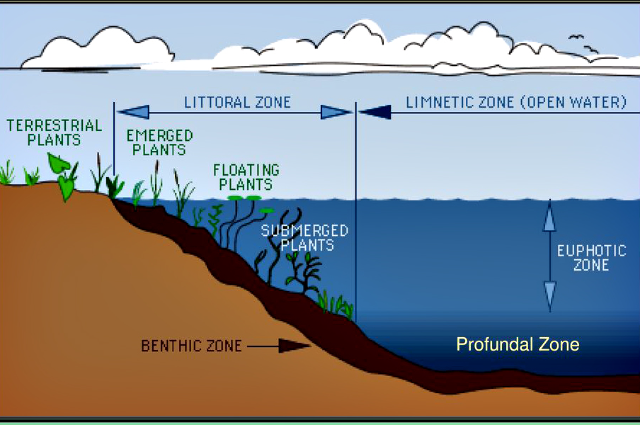
Four distinct zones are prominently divided into freshwater bodies; divisions are given as follows:
- Litoral zone: Shallow (not very deep) zones, situated very close to the land, where sunlight can penetrate up to the bottom level of the water.
- Limnetic zone: This zone occupies the same depth as the litoral zone but unlike the litoral zone; this zone is situated away from the land.
- Profundal zone: This zone occupies a slightly deeper region than the other two zones; due to depth sunlight cannot penetrate up to the bottom level of the water; i.e. just exhibits the opposite characteristics of the previous two zones.
- Benthic zone: This zone is composed of the sediment of mud, rock, and organic matter and it is the bottommost layer of water bodies. This zone is generally oxygen deficient.
Some important parameters control the overall (not only the structural part but also the functional part) scenario of freshwater bodies; they are nutrient quality, organic content, oxygen concentration, and temperature.
The nutrient status of water bodies is mainly affected by two major elements; Phosphorus and Nitrogen. When sufficiently large amounts of these two elements are added to the water, that particular water body (lakes, ponds) becomes enriched with nutrients; this phenomenon is called eutrophication and those nutrient-rich lakes and ponds are called eutrophic lakes. These eutrophic lakes provide a hostile environment for the growth of many bacteria but at the same time, the same environment becomes friendly with algae and supports their growth. Sometimes, Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) may compete with other algae in the presence of extra nitrogenous and phosphorus compounds.
Simultaneously, oligotrophic lakes(nutrient deficient) also can be converted into eutrophic lakes by the action of Cyanobacteria; they are capable of nutrient accumulation in the presence of phosphorus.
Organic compound is another major contributing factor to the development of microbial flora in freshwater bodies. Actually; those Organic compounds determine the BOD value of water(Biological Oxygen Demand) by following a standard law;
- Higher BOD value = Concentration of organic compound is high = water sample is highly polluted
- A high concentration of organic compounds actually encourages the growth of decomposers (Fungi successfully play the role of decomposer).
- Oxygen concentration is directly proportional to the BOD value of water; a higher BOD value means, more oxygen has been consumed by aqua lives.
- The temperature of the freshwater body lies down to the extreme range(0-90˚C) and respective microbes are found throughout the range.
Microbes induce water pollution - Is it true? Or something else? Let’s see!
This above statement is partially true. Not only microbes alone, several physicals (soil, sand, rock, stone), as well as chemical compounds(nitrate ion, benzene, arsenic, carbamate compounds, fluoride ion), properly cooperate with them.
The major disturbing microbes present in the water sample are coliform bacteria. They act as the pollution index of water. According to BIS (Burro of Indian Standard); any water sample can be regarded as safe for drinking purposes if it contains coliform bacteria less than 1 per 100ml.
Coliform bacteria are one of the problem-creating microorganisms present in the water, although they are not so harmful by means of themselves; their presence in the water sample indicates that other pathogenic microbes must be present in that particular water sample. Due to this unique property, coliform bacteria are considered “index organisms of water pollution “
This is high time to be informed about coliform bacteria, otherwise a big question mark will arise regarding human health.
Some basic characteristics of coliform bacteria are highlighted here:
- Gram-negative, Rod-shaped bacterial group; belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family.
- They are non sporulating (non spore forming) bacteria.
- They can produce acid and gas simultaneously by fermenting carbohydrates.
- Ex: Lactose Broth Lactic Acid+ CO2
CLASSIFICATION:
On the basis of their habitat, coliform bacteria can be categorized into two types:
- Fecal coliform (present in human feces )and
- Non-fecal coliform (present in the soil, grass, etc. Other than human feces.)
Detection of the presence of coliform bacteria in the water sample:
Two Consecutive tests have been performed to achieve the goal; one of them is the Presumptive test.
- Presumptive test: According to the name, by performing this test we can presume/assume the presence of coliform bacteria in the water sample.
- To perform this test we should use water samples from different sources; i.e. pond water, tap water, and mineral water (at least 3 samples).
- Lactose Broth media should be used also.
Now inoculation (mixing of media and water sample) should be performed in the following way:
- 10 ml Lactose Broth+ 10 ml water sample
- 1 ml Lactose Broth+ 1 ml water sample
- 0.1 ml Lactose Broth+ 0.1 ml water sample
INCUBATION PERIOD:
24-48 hrs(Tubes should be kept inside incubator at 37˚C temperature)
DETECTION:
Gas production occurs inside Durhum’s tube after 24 hours of incubation; it is detected by the presence of air bubbles. The intensity of gas production is directly proportional to the number of air bubbles. This is a positive result.
If the result of the presumptive test comes back positive, only then we will continue the remaining portion; and confirm the test. If the result of the presumptive test comes negative; that indicates two major informations:
- That particular water sample may be pure; and not contaminated with any pathogenic microbes including coliform bacteria(Ex: Mineral water).
- That particular water sample may be contaminated with pathogenic microbes other than coliform bacteria. (Ex: Tap water).
Pictures of this experiment are given in the following:
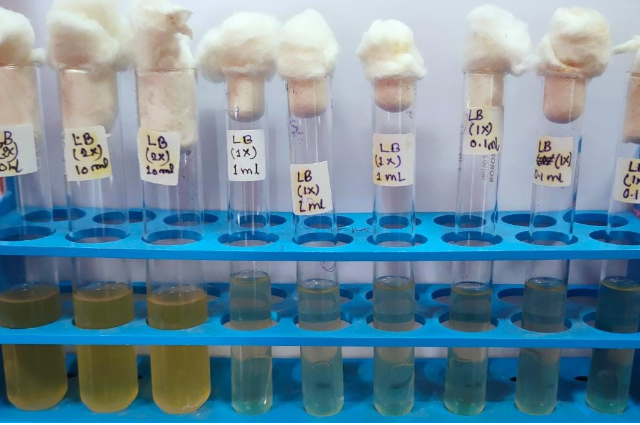
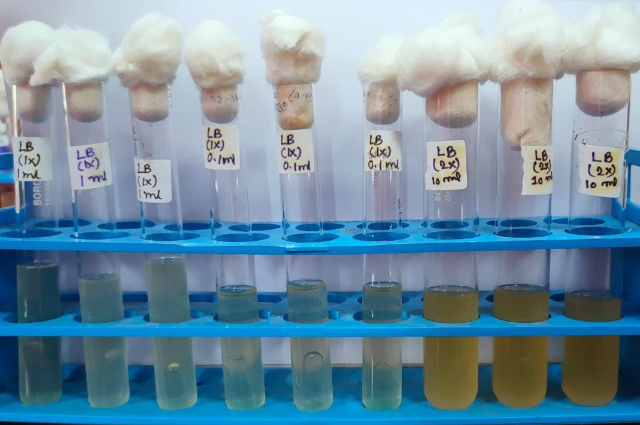

- Fig A: Lactose Broth containing tubes, the prominent bubble is present inside it. Therefore, Figure A indicates a positive coliform test.
- Fig B: The same media (Lactose Broth) is present, but there is no prominent bubble. Hence, Figure B indicates a negative coliform test.
[Both snapshots have been taken during lab experiment of mine]
Finally, we can conclude the topic by keeping some important information in mind that:
- The drinking of pond water should be avoided; especially in remote rural areas, where all household things like cloth washing, utensil cleaning, and bathing of cattle animals have been performed regularly.
- Dumping of any domestic wastes into water bodies should be strictly prohibited.
- Personal hygiene should be maintained properly always(washing hands with soap, using sanitizer, etc)
- Water should be filtered at least by domestic method before drinking.
In the end, as water creates as well as saves the lives of all living creatures, for our own benefit we should not make the water polluted instead of preserving it.