In the words of Charles F. Hannel,
“Every cell in your body is intelligent and will respond to your direction. The cells are creators and will create the exact pattern which you give them.”
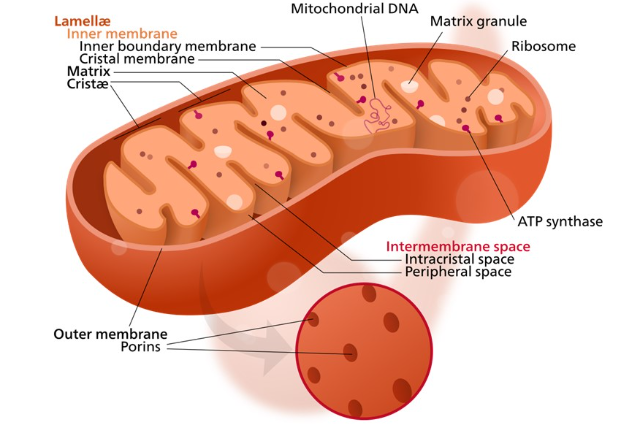
Mitochondria are referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria help in the survival of the cell by producing energy. Mitochondria perform cellular respiration and convert energy into a form that is used by the cell. This requires oxygen and release of carbon dioxide as a waste product.
Why mitochondria are so important for cells?
- Mitochondria help in calcium homeostasis: It stores calcium and works with other organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum and extracellular matrix and helps in the balance of calcium ion concentration. Calcium homeostasis is important for the physiological and pathological mechanisms of the heart.
- Mitochondria help in the regulation of innate immunity: Mitochondria can regulate the activation of immune cells, their differentiation, and survival. They modulate the metabolic reprogramming into pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory subtypes of immune cells. Other ways to regulate innate immunity are anti-viral signals, anti anti-bacterial immunity by generating Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS).
- Mitochondria's role in programmed cell death: Programmed cell death is called Apoptosis through an event known as Mitochondrial Outer Membrane Permeabilization (MOMP). The event causes the release of protein from mitochondria intermembrane space and results in the regulation of caspase activation. Therefore, leads to cell death.
- DNA repairing: Mitochondria play a role in repairing oxidative DNA damage. Base Excision Repair (BER) is a pathway through which small DNA gets repaired and by alkylation, deamination, or oxidation DNA gets modified.
Does Mitochondria have its DNA?
Yes, Mitochondria have their DNA which is mtDNA that is Mitochondrial DNA. It is circular and double-stranded and different from DNA in the nucleus. As Mitochondria play a very important role in a cell by regulating various events what do you think Is it possible for the cell to survive without Mitochondria?
A living cell without Mitochondria - The Oxymonads:
All eukaryotes like plants, fungi, and animals are made up of cells having mitochondria, with the help of the mitochondrial electron transport pathway this organelle generates extremely important energy that provides the ability for cells to function properly. But, according to the new research oxymonads that is single-cell protists found in the gut of the insect (wood-eating termites) and the gut of animals. Oxymonads are flagellated and club-shaped cells. Their size lies between 5-165 microns. They are dependent on the host for their nutrition. Oxymonads can survive without mitochondria. It has adapted to survive without Mitochondria by developing alternative mechanisms for the production of energy. Mitochondria play a vital role in the production of energy, help in the regulation of metabolism, and also promote the growth and multiplication of cells.
Adaptation made by Oxymonads:
Oxymonads have survived without Mitochondria by adapting to anaerobic conditions. They have accomplished bacterial Fe-S cluster synthesis and assembling in the cytosol. Hence, making them adapt to anaerobic conditions. Some species have developed a sulfur mobilization system from the bacteria. New studies have given different protest classifications like Archaeplastida a plant super group.
Studies justifying the survival of Oxymonads with the help of metabarcoding:
Mitochondria were considered to be important for the survival of eukaryotes But it was discovered that protists like Oxymonads that live in the intestine of Chinchilla survive without mitochondria. New studies have been carried out on the ssu rDNA (small subunit ribosomal DNA). It is a gene used for metabarcoding of species of Oxymonads and Trimastix which is almost identical to Oxymonads. This study revealed that these two groups are similar and concluded them as sister groups. This leads to the renovating of theories on eukaryotic phylogenic tree
Similar species of Oxymonads - without mitochondria:
Trimastix do not carry mitochondria but are found to have mitosome which is a double membrane organelle. As such there is no proof to justify the fact that it produces ATP, but mitosomes have glycolytic pathways. Investigators found that Oxymonads are surviving without mitochondria from the age of dinosaurs. Oxymonads can evolve into new species without the powerhouse Mitochondria.
Conclusion:
The message is clear from the above discussion that the powerhouse of cells can be adapted or completely replaced by eukaryotic cells. There we can clearly say that,
“Eukaryotic cells can survive and thrive without mitochondria”.