
The amount of critical diseases is frequently expanding in the entire world, and even, India is no exception to it. A disease like cancer which has various types like skin, brain, and breast cancer has created troubles for several countries. And in that, skin cancer comprises a slight but crucial percentage of patients with cancer. In India, skin cancer comprises less than 1-2 % of all analyzed cancers. Although the presence of ‘Eumelanin’ in dark skin is defensive against the growth of skin cancer, it is increasingly being analyzed in the Indian population. ‘Basel Cell Carcinoma’ is the most common form of skin cancer worldwide, but distinct research from India have invariably noted Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) as the greatly prevalent skin cancer. This type of skin cancer is caused by the uncontrolled expansion of unusual squamous cells.
Skin cancer is the most widespread type of cancer which is caused largely due to excessive revelation to ultraviolet rays from the Sun. Some complicated surgeries, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and other conventional therapies are the common treatments for skin cancer, with several limitations. But a team of researchers from Bangalore has created a simple and beneficial way to cure it by developing a skin cancer bandage. Researchers from the Center for BioSystems Science And Engineering (BSSE) and the Department of Molecular Reproduction, Development and Genetics (MRDG) at the Indian Institute of Science (IISC) has developed a non-interfering dressing made with magnetic nanofibers to treat skin cancer by conducting heat to the cancer cells by utilizing a skin cancer bandage.

IISC said in a declaration that a favorable option that has appeared as skin cancer is utilizing ‘Hyperthermia’. It encompasses applying heat to the affected tissues. The IISC researchers have been operating on formulating ways of transmitting heat to the cancer tissues so that cancer cells are targeted selectively and effectively. This kind of technology is called magnetic hyperthermia, in which magnetic nanoparticles are utilized to heat the tumors by obtaining an external Alternating Magnetic Field (AMF). When researchers found that it was tough to achieve uniform heating on the affected tissues, they created a bandage with a special mixture of magnetic nanoparticles fabricated utilizing a method named electrospinning. This bandage that can cure skin cancer comprises nanoparticles made from an oxide of iron, Fe3O4, and a biodegradable polymer named polycaprolactone (PCL). The magnetic material produces heat when it is subjected to a high-frequency magnetic field.
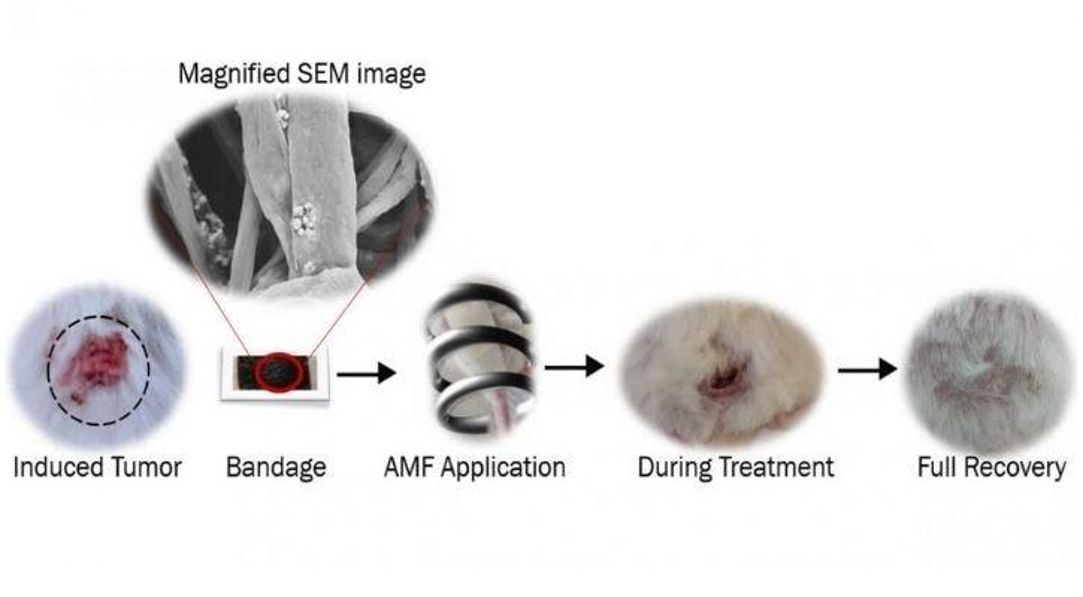
To make conclusive results about its usefulness, researchers did two experiments, one was in vitro, which is on human cancer cell lines and the other was on vivo, on mice with artificially-provoked skin cancer. In both examinations, magnetic skin cancer bandage destroyed cancer cells completely.
This type of modern cancer treatment by a skin cancer bandage is incredibly beneficial against skin cancer in lab tests. But it is still at a developing stage as a clinical therapy. IISC has announced that further research are assigned to test the usefulness of this method on a bigger scale in rabbits, dogs, and monkeys before utilizing it for pre-clinical and clinical requests on humans. But this evolving and encouraging way to cure skin cancer with skin cancer bandage is providing hopes and faith to the skin cancer patients and healthcare departments of the country.
___________________________________________________________________
Reference:
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- www.indianjcancer.com
- www.theswadle.com
- www.iisc.ac.in
