Background:
Romantic poetry was a style of poetry developed in Europe in the 18th century and later adopted in America. Despite the name, Romantic poetry was not necessarily concerned with romance or romantic love as it's subject matter. The 18th century Romantic poetry was in many ways a reaction to the Enlightenment's fascination with reading and science. It was also largely inspired by the French Revolution and other self-determination movements in Europe at the time.
Romanticism:

Understanding the historical background of Romantic poetry requires a more detailed explanation of Romanticism in general. Romanticism was a poetic, musical, and artistic movement that was concerned with operatic emotions and individual experience. Artists and poets of the Romantic era were interested in how individuals perceived the world instead of rational evidence of how the world actually was. They wanted to uplift, celebrate, and explore the biggest emotions that humans could experience namely love, grief, awe etc. Much of Romanticism was concerned with the interplay between the beautiful and the sublime, with the sublime being favoured in most cases. There were several famous Romantic poets who left their mark on poetry forever. The Romantic Movement originated in England before later expanding. Romanticism was just started by two writers - Samuel Taylor Coleridge and William Wordsworth. They all were deeply connected with each other and they all fit into different generations of Romantic poetry.
Themes of Romantic Poetry:

The Romantic writers were interested in similar ideas and had similar ways of approaching them. Emotion, sublime and individual experience were important parts of Romantic poetry. Other important themes included such as revolution, the natural world, mortality and transcendence. Most romantic poets shared enough similarities and self-conscious imitation of each other's forms that they belong to the same literary movement. It is characterised by everyday language, explorations of morality, high levels of emotion and themes of revolution and liberation. It is not necessarily connected to romantic love. Instead, they were much interested in the human experience, transcendent mental state and intense emotions.
Various Romantic Poets:
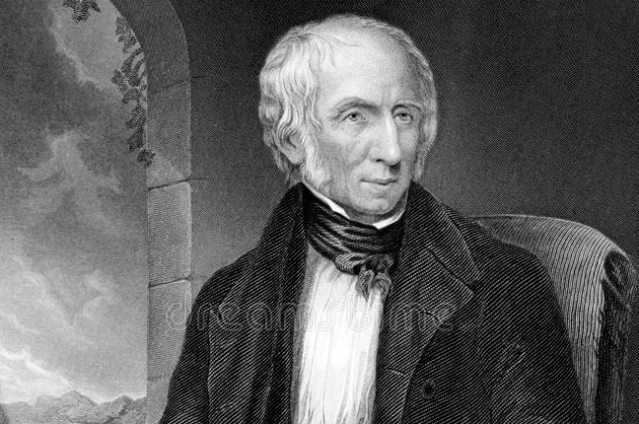
(1) William Wordsworth (1770-1850)
He was one of the great protagonists of the Romantic Movement. His idea was to make natural things appear unnatural, by adding to them the light that never was on sea or land. He had therefore to give charm of novelty to everyday things and to produce a feeling analogous to the supernatural by freeing the mind's attention from the lethargy of custom and directing it to the beauty and wonders of the world before us. William Wordsworth used his imagination to make things appear as supernatural. The common objects seems to be completely changed and transmitted. The addition of a sense of strangeness to the ordinary beauties of life and making of ordinary thingd to look as extraordinary. He used to write freely from the set fixed rules or regulations. He was of the opinion that the writers should be free from any destruction and should express their thoughts which arise in their mind. Wordsworth took up new subjects of poetry. His adoration of nature and common life wtew things of romantic character. He elevated nature to the dignity of adoration. His mysticism was something new which poetry world had not experienced before. The poet viewed the spirit of God pervading the entire universe both animate and inanimate. He saw the presence of the power of God in Nature and in human life. His insistence on the use of simple language in place of difficult words are again some important strides. His numerous lyrics, odes, sonnets were also romantic in colour. The imaginative supremacy and emotional excitement were introduced by the Romantic poets. Thus, Wordsworth was one of the great protagonist of the Romantic Movement. Some of his famous creations are 'Daffodils' and 'The Prelude' etc.
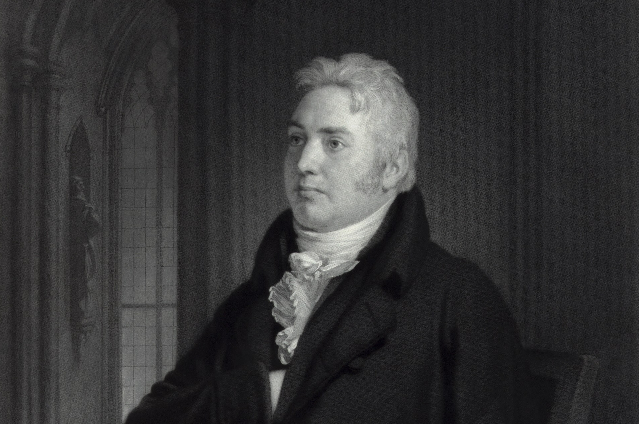
(2) Samuel Taylor Coleridge (1772 - 1834)
Coleridge was a co-founder of Romanticism in English Literature. His famous creations are, 'Kubla Khan' and 'Frost at Midnight' etc. In his rich romantic imagination, suggestiveness, symbolism, love of the nature, fascination for the remote, treatment of the supernatural and the dream quality of his poetry. His poetry is the most finished, supreme embodiment of all that is the purest and the most ethereal in the romantic spirit. Coleridge broadened the sphere of music to the intellectual side of the movement. Coleridge held a higher ideal of poetry and fought bravely against the artificial style of the previous age. The simplicity of language, the flight of imagination, love of nature, humanitarian and democratic outlook were all the qualities in the creations of Coleridge. He could conceive and perceive both the natural and supernatural. For him, the real world was a world of fixities and only the imagination of the poet could make it worthy of appreciation. He pleaded for the importance of individual mind and power of imagination in the most forceful words. He rejected reason and preferred impulse and imagination. Coleridge has been recognized as a ballad writer. His poems give a sense of Nature. He attributed Nature to an independent existence capable of comforting human beings and exterting them a salutary moral influence. He gives a new turn to supernatural happenings by presenting them as phenomena of the mind and what is excited in the mind by the passions. Spirituality has also been seen in Coleridge's poetry. His creations communicate the moral truth. Still, the psychology of the poet helps in conveying a lot about the subject-matter.
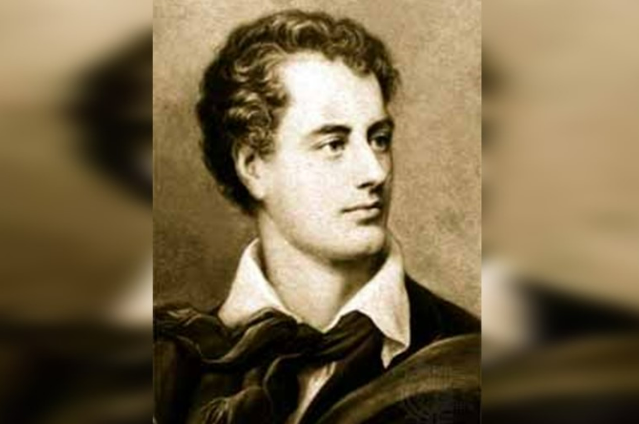
(3) Lord Byron (1788-1824)
He was a well known Romantic poet of the Second Generation. His famous creations are, 'Childe Harold's Pilgrimage' and 'Mazeppa' to name a few. His Romanticism was very different and deviated from it's original essence somewhat. He wrote many satires till the end. He was engaged with the materialism of life as well as the interior exploration of poet's feelings for sujectivity. He transcends his materialistic thoughts into his own poetic experiences. He perceives the material from the society, georgraphy and political aspects of Europe and translates it to his own poetical experiences. The realm of Europe is the sensuous place for Byron and a place of knowledge. His writings are unconventional. He combined the rational elements with spirit of Romanticism to form a new work of Romantic art. He shrouds the classical essence in his writings. He was critical of his own contemporary age. He mocks at the aristocratic rules of education. Byronic heroes are passionate, charming and mysterious etc. It seems that the country of Europe is the place of emotional attachment or a peace or sensousness where Byron seems to emphasize upon.
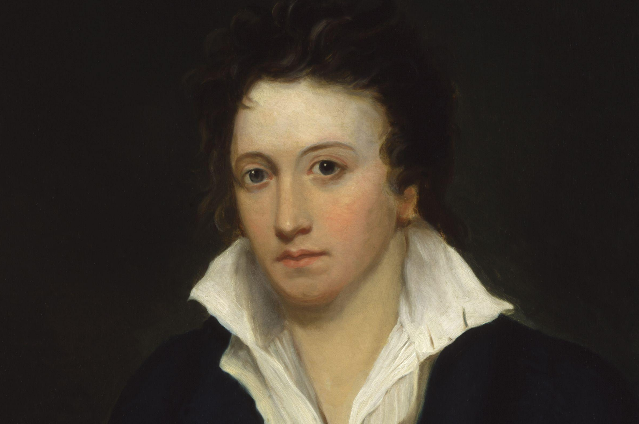
(4) Percy Bysshe Shelley (1792 - 1822)
He belonged to the Second generation of the Romantic Age. He became a key member of the close knitted circle of visionary poets. He is known for his classic poems such as, 'Ode to the West Wind', 'The Cenci' and 'The Cloud' and others.
His writings feature holds the prospects of mysticism. He explores the realm of inexistent beings rationally and it's manifestation on human mind. The unseen power is being referred to as the 'Spirit of Beauty' which he further adds that it's manifestation on human mind can make any individual omnipotent and extremely power. His use of satire was directed ahshnst the political tyranny and rulers. The faculty of imagination is expressed as closely resemble to the divine. However, his amalgamation of facts and nature add to his creative imagination. Shelly was a revolutionary post and derives much influences from the French Revolution. He talks about the closure of an existing social order resulting in harbingers of change. Lastly, Shelley exhibited Hellenistic culture writing in his poems.
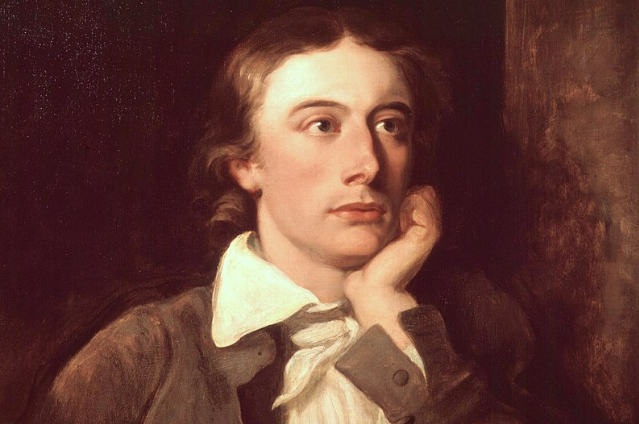
(5) John Keats (1795 - 1821)
John Keats is in many ways the most romantic of all romantic poets. Keats through his poetic expression soughts an escape from the world. The poet seeks an escape from the hard realities of life in a world of romance and beauty. Keats is the most romantic of all the poets in the sense that he is most escapist of them all. Most of his poetry is inspired by the past. It is rarely that he devotes himself to the pressing problems of the present. Keats thus find an escape into the past from the oppressive realities of the present. Most of his poetry is devoted to the quest of beauty, love, chivalry, adventure- these are the main theme of his poems. The fear of death haunts him constantly and which finds beautiful expression in his sonnet. Another favourite theme of his poems is disappointment in love and it's desolation. He has a vivid sense of colour and transfigures everything into beauty. Beauty for him is synonymous with Deity or Truth. A thing of beauty is for him a joy forever. Beauty is his religion. It is in the pursuit of this beauty he completely forgets himself and the world around him. He adds some strangeness to beauty. Keats sees beauty in the ordinary things of nature. The earth to him is a place where beauty renews itself everyday. Keats loved all the mighty abstracts of beauty. The song of the nightingale becomes a symbol of the universal spirit of Beauty. Pursuit of the unknown, the invisibe and infinite inspires the creation of Romantic poetry in the world. For Keats, the nightingale is a symbol of unlimited joy and happiness. His poetry is full of unique suggestive expressions. The brief span of Keats life fell within, what is known as the age of Romantic Revival in English Literature. His famous poems are, 'Ode to a Nightingale' and 'To Autumn'.
(6) William Blake (1757 - 1827)
He is considered as a precursor of Romanticism in English Literature. His famous works are, 'A Divine Image', ' A Poison Tree' and 'The Garden of Love'. Poetry initially suffered from an excessive adherence to rules and monotony of heroic couplets. All literature was confined to some established classical norms. Blake emphasised on being true to your imagination and also brought a drastic revolution in the sector of diction. The poetic creed of William Blake is based on imagination. Blake's nature of work is visionary or imaginative and it is an endeavour to restore the Golden Age. Blake held that it is the artist's business to attain this heightened view of things and show us what kind of world is actually in front of us, with all it's growing splendour. He also broods over the spiritual freedom or spiritual salvation of mankind. Blake vehemently argues for the freedom of human energy too. He us regarded as the Prophet of Spiritual Liberation and his Mysticism. Contrasting aspects of human heart which constitute the whole of man's life and work for the salvation of soul. Nature has been associated with rejuvenating stimulants. His nature is a part of the human universe and symphathises with the human. Blake's symbology is too large and complex to be given in brief. He uses allegory which according to him presents events in a spiritual world. According to Blake, the world of imagination is the world of eternity. Indeed, he was a champion of Romantic poetry in 19th century in England.
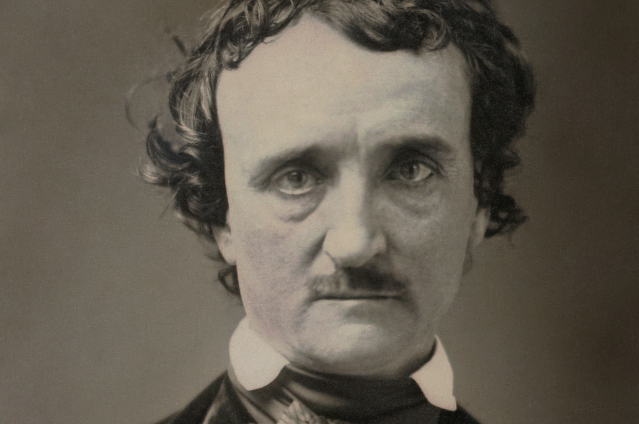
(7) Edgar Allan Poe (1809 - 1849)
He is the most famous in the Dark Romantic authors in American Literature. He left a significant impact on American literature. Dark Romanticism is a literary subgenre of Romanticism. Dark Romanticism evolved from the combination of both Romantic and Gothic elements. It is a gloomier form of Romanticism. While Romanticism glorifies the inherent sublimity of human intentions, Dark Romanticism is characterised by a pre-occupation with emotions like apprehension, fear and aspects of imagination. The motives behind Dark Romanticism belongs to the realm of uncanny where love becomes lust, nature becomes mist and lightning and buildings often feature haunts and ruinations. Edgar Allan Poe was a Romantic who worked in the Gothic mode. His poems and stories explore the darker side of Romantic imagination, dealing with the mysterious, supernatural and horrifying. Some of his famous creations are, 'The Raven', 'Alone' and 'The Sleeper'.
Characteristics of Romanticism:
- Celebration of Nature: Romantic writers saw nature as a teacher and a source of infinite beauty. One of the most famous contributions here is of John Keats.
- Focus on the Individual and Spirituality: Romantic writers valued their inward experience the most. This led to the heightened sense of spirituality in Romantic work. The work of Edgar Allan Poe exemplifies this aspect of the movement.
- Celebration of Isolation and Melancholy: Related to the insistence on isolation, melancholy is a key feature of many works of Romanticism. This has been well seen in the works of Percy Bysshe Shelley.
- Interest in the Common Man: William Wordsworth was one of the poets to embrace the concept of writing that could be read, enjoyed and understood by anyone. He favoured simple and elegant language for the understanding of the most common person out there.
- Idealization of Women: In the works of Jane Austen such as, the women were always presented as idealized love interests, pure, beautiful but usually without anything else to offer. Most Romantic literature is infused with the concept of women being perfect innocent beings to be adored, mourned, and respected but never touched or relied upon.
- Personification and Pathetic Fallacy: Mary Shelley used these techniques to influence the literature. It largely emphasises on the fixation on nature. Thus, incorporating everything around it in the discussion.
Conclusion:
Romanticism was thus a cultural movement which sought to develop a particular form of nationalist sentiment. It focused more on emotions, intutions and mystical feelings. Their effort was to create a sense of shared collective heritage, a common cultural past as the basis of a nation. Thus, Romanticism continues to be regarded as an important development in the field of literature.