Introduction
Every person aspires to own a car, motorcycle, jeep, etc. The number of vehicles on the road has increased so have the road fatalities and mishaps, which has resulted in India being a top accident-prone country. The legislation has taken a major attempt to amend the motor vehicle act, which enhances stringent punishment and penalties for driving errors or violations of provisions.
It has also included a provision where a guardian or the owner of the vehicle is liable for an accident caused by a juvenile, provided a scheme for cashless treatment to the victims of road accidents, during the golden hour, and ensures road safety. Central government has incorporated Road Safety Board under section 215D who looks into the matters and advice Centre and State government in every aspect of road safety, traffic management, rules and regulations that includes standard of vehicle, compulsory registration of the vehicle, licensing and promoting new vehicle technology.
Salient features of the Motor Vehicle Amendment Act 2019
Compensation for road accidents
Under section 162(1) of the motor vehicle act, the central government has introduced a scheme of cashless treatment for the victims of road accidents., during golden hour. Golden hour is the period lasting for one hour following the traumatic injury where the chances of surviving the victim are high, by providing proper medical care or assistance that would prevent the death of such person.
Good Samaritan
A Good Samaritan is a person who voluntarily, in good faith, without expecting any sort of compensation or reward, provides emergency medical or non-medical care or assistance at the place of occurrence of an accident or transports such person to the hospital. In such case, a good Samaritan under section 134A shall not be liable for any civil or criminal action or harassment by any official for any injury or death of the victim or such injury or death caused by a good Samaritan’s negligence or failure to act while rendering services.
Motor Vehicle Accident Fund
Motor vehicle accident fund has been introduced under section 164(B) to give immediate relief to victims of a motor accidents and hit and run cases or that fund shall be constituted for providing compulsory insurance to all road users in India
Compensation in case of hit and run cases under section 161, has been increased from Rs. 25000/ to Rs 2,00,000 in respect to the death of a person and case of grievous hurt, compensation has increased from 12,500 to 50,000
Violations of road regulations
Section 177 states-general provisions for penalties for various traffic rule violations. As per the section, whoever breaches any provision, rule, or regulation of this act, or if no penalty is provided for such breach or contravention shall be punished with a fine that may extend to Rs.500 for the first offense and for subsequent violation fine that may extend to Rs.1500/ or both. It includes offenses like operating a driving school without a license, failing to obey the traffic signals, not following prescribed signals, or allowing someone to obstruct your vehicle’s control. Amendment has increased the monetary fine from 100 to 500 and 300 to 1500 respectively.
Compulsory insurance policy
If you are thinking to avoid motor vehicle insurance or planning to drive an uninsured vehicle, you are merely digging your own grave. Because the amendments made in the Motor vehicle act are more stringent and driving an uninsured vehicle would surely land you in jail.
An insurance policy will secure you against any unpredictable incident and keep your vehicle financially covered against damages or theft. Be it a two-wheeler, car, jeep, or truck; insurance is mandatory. This act under section 164B comprises a Motor vehicle accident fund for providing compulsory insurance to all road users in India. That fund is utilized for the treatment of the victim injured as per the golden hour scheme, compensation is provided to victims in case of grievous injury or legal representatives of victims who have died in a hit and run cases.
- According to section 196 of the motor vehicle act 2019, if you are found driving an uninsured vehicle, then you are penalized an amount of two thousand rupees or imprisoned for up to three months for the first offense and a second subsequent offense, a fine of four thousand rupees or imprisonment up to 3 months or both.
Third-party insurance:
Third-party insurance is an insurance policy purchased by the insured for protection against the claim of another party. The central government has also made schemes for providing interim relief to claimants seeking compensation under third-party insurance.
Recall of motor vehicle:
The central government under section 110A of the motor vehicle act 2019, is allowed to direct a manufacturer to recall his manufactured vehicle of a particular variant if any defect in the vehicle causes harm to the environment or the driver or other pedestrians. Such manufacturer will be required to recompensate the purchaser's full cost of the vehicle or replace the defective vehicle with a new vehicle of better descriptions or quality.
Offenses and penalties
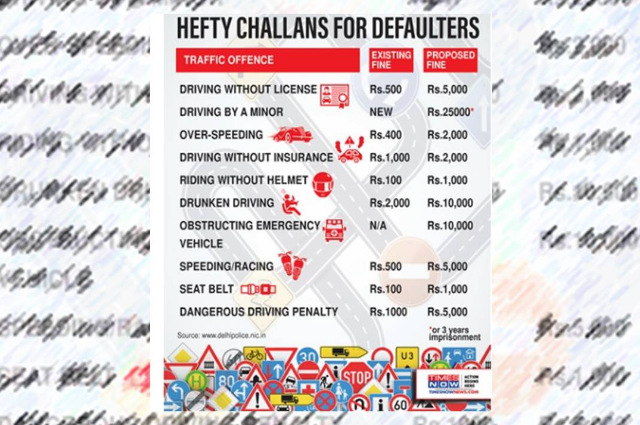
- Disobedience of an order: Section 179 of the motor vehicle act 2019, if anyone is caught disobeying orders of authorities, that person will be fined Rs. 2000.
- Allowing an unauthorized person to drive a vehicle: Under section 180, if any person makes unauthorized use of a vehicle without a license will be punishable with a fine of five thousand rupees and imprisonment for a term which may extend to three months, or with both.
- Driving without a license: Whoever drives a motor vehicle without having a valid license shall be punishable with imprisonment which may extend to 3 months and a penalty of five thousand rupees, or with both; under section 180 of the amended act.
- Driving despite disqualification: Under section 182, if a person drives a vehicle despite his disqualification under the Act shall be punished with imprisonment for a term of 3 months and a fine which has increased from 500 to 10000.
Under section 182A punishments related to offenses, where a manufacturer, seller, or dealer fails to comply with the motor vehicle standards will be punishable with a fine of 1 crore and imprisonment for a term of one year. - Over speeding: Over speeding the vehicle is responsible for most of the accidents on the road, which are dangerous and fatal for both drivers and other road users. If you are found driving a vehicle at excessive speed, under section 183, a penalty of Rs. 1000 that may extend up to Rs.2000 for lightweight motor vehicles that include bikes, cars, rickshaws, and a penalty of Rs. 2000 to maximum Rs. 4000 for medium or heavy passenger vehicles for their first offense. For a second subsequent offense, the driving license of that person may be confiscated.
- Dangerous driving: Racing, driving aggressively, speeding, violating traffic signals or jumping red lights, using a mobile phone while driving, and chasing another vehicle to compete are examples of dangerous driving. Under section 184, offenders driving dangerously will cost a penalty of Rs. 5000/ with six months’ imprisonment for the first offense and a subsequent offense, imprisonment for 2 years with a fine of Rs. 10,000 or both.
- Driving under influence of alcohol: Drink and driving or any person who drives under influence of alcohol are punishable under section 185, which cost an offender a fine of up to Rs. 10000.
- Driving vehicle without registration: Every vehicle you owe must be registered under the motor vehicle act. It is illegal to drive an unregistered vehicle. As per section 192 of the motor vehicle act, 2019 the amount charged for driving an unregistered vehicle is Rs. 5000 and if you are again found driving without registration, you will be fined Rs. 10000 and imprisonment are not less than 1 year.
- Overloading:
| Section | Offence | Penalty as per |
| 194 | Driving a motor | A penalty of Rs. 2000, Rs.2000 per extra toe. He is also liable to pay extra charges for |
| 194A | Overloading | A penalty of Rs.1000 |
| 194C | Overloading | A penalty of Rs. 2000 along with |
- Seat belts: Wearing a seat belt is essential for the driver as well as the passenger riding in a motor vehicle. Seat belt reduces the risk of death by 45-50% among the front seat passengers and the driver and serious injury among rare occupants by 25%. If a driver is found driving his vehicle without wearing a seat belt, will be punishable under section 194B with a fine of Rs. 1000.
- Penalties for not wearing protective headgears: Protective headgear means a helmet that is used to protect the head in the event of an accident. Proper use of helmets can reduce the risk of fatal injury by 42% and head injury by 69%. Riders driving two-wheelers without a helmet are fined Rs. 1000 and can also suspend your license for 3 months under section 194D of the motor vehicle amendment act.
- Failure to provide a way for emergency vehicles: Whoever fails to provide free passage to emergency vehicles like fire brigade, ambulance or other emergency services on the road will be punishable under section 194E of the act with a fine of Rs. 10,000 and imprisonment that may extend up to 6 months.
- Use of horn: Under section 194F, whoever while driving a vehicle makes unnecessary and continuous use of horns in silent zone areas or places, where traffic signs signify prohibiting the use of horns, shall be punishable with a fine of Rs. 1000 and for a second subsequent offense fine of Rs. 2000
- Offences by juvenile: Motor vehicle amendment has included stricter punishment for guardians in the case where the accident is caused by a juvenile. As per section 199A, the guardian or the owner of the vehicle is held liable for the offenses or accidents caused by a juvenile. The guardian has to pay a fine of Rs. 25000 and may also face imprisonment for a term of three years. Registration of the vehicle is also canceled for one year.
Exception: This section would not be applied to a juvenile who already has a learner’s license.
Implementation, fines, and penalties.
Maharashtra government implemented the motor vehicle act, of 2019 and has hiked the compounding fines and penalties for traffic violations by issuing a notification which came into effect from 1st December 2021. It is believed that implementation will bring an overall discipline among the citizens and curb accidents and road fatalities and ensure road safety. The compounding fee is in the range of Rs. 200 to Rs. 1 lakh for different offenses.
A sooty rider in Gurgaon was fined Rs. 23,000 for a traffic rule violation. He was fined Rs. 5000 for driving without a license, Rs.2000 for driving without insurance, Rs. 10000 for not carrying PUC, Rs. 1000 for driving without a helmet, and Rs 5000 for driving without a vehicle’s registration certificate. Also read: new traffic Rules & fine in India
Conclusion
Motor vehicle act,2019 was amended to make roads safer and to advance the significance of safe driving among the youth who often get penalized due to rash driving, overspeeding, driving without a license, etc. Punishments for traffic violations have become significantly stringent. These punishments create deterrence in the mind of people and make them more responsible to follow rules and regulations.
Reference:
- www.who.int
- blog.ipleaders.in
- www.magzter.com/stories
- m.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge
- www.indiatvnews.com