"Do or do not. There is no try" - In the Irvin Kershner-directed movie Star Wars Episode V: The Empire Strikes Back, Yoda, who is portrayed by Frank Oz, utters this phrase (1980).
The context mentioned above was spoken in 1980, however, the year is already 2022. The world is awash in technologies, and more are constantly being developed.
What Yoda's Context Really Meant to People?
A small story,
The context meant Yoda's sense of reality at that time(on 1980s). There are typically only two actual outcomes in life: success and failure. However, in fact, you either succeed or fail. It doesn't operate that way; there is no outcome termed "try" where you both succeeded and failed. We aren't born with the intrinsic ability to do everything in life, thus failing is also totally acceptable. Simply said, I'm physically unable of doing it since I lack the necessary muscle mass. Simplest terms, I am physically unable of doing it since I lack the necessary muscle mass and would inflict harm on myself if I tried. The long view is another option, though. As long as I keep "doing," as in training and moving up the ladder, I will eventually succeed and I can just think of it as one big assignment in which there were a lot of minor successes and failures.
The bolded words says the meaning of the saying!
Conclusion about Yoda's words:
"If you do something, the probability is either win or loose, but we don't know the outcome, at the time of trying. He says, don't waste your energy, time by just trying out something, if you do so, you will definitely loose something either time or energy. Here, comes the technology, that people should try whatever they thought, without any care of loss."
So, that the winning probability will be more, right? without any loss. All those tries are counted as experience Interesting right?
Extended Reality (XR)
Let's assume for a second to better understand what we're talking about. Have you ever walked through a museum wearing headphones that provide an audio experience? It sounds like you are suddenly in the Wild West or wherever this encounter is taking place.
Add images and additional interactive features that can be touched. While walking down the sandy road, you might be able to touch the saloon's doors or see the sceneries alter. For a duel, you can draw your pistol.
Consider experiencing these things even when you are not in a museum. You might find it in your own backyard or the market street in your city. The virtual world has melded with your reality. You have extended your reality, that's XR. Wow, right? Just as we were proposing, Extended Reality (XR) renders all of this attainable.
“A mind that is stretched by a new experience can never go back to its old dimensions.” — Oliver Holmes, Jr.
Introduction:
A new environment where real and virtual items are blended at various levels is being created through the introduction of virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed-reality technology. The customer experience environment is changing into new kinds of hybrid experiences as a result of the development of portable and embodied gadgets together with highly interactive, physical-virtual linkages. However, researchers and practitioners have not yet properly defined the boundaries between these new realities, technologies, and experiences.
Extended reality is abbreviated as X reality(XR). The collision of the actual, real world we live in and a digital realm is sometimes referred to as cross-reality.
Combining a digital or virtual experience with a physical one is one way to approach the issue. There are numerous possible outcomes, but as technology advances, the possibilities multiply.
Powerful components of XR:
Augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) can all be grouped under the umbrella term "X reality" (XR), however, it is not limited to these three. XR can also refer to any human-computer interface that is in development or already in use that expands on the relationship between graphic technology and wearable technology. The potential for inclusivity and growth is great because this field encompasses such a wide range of human experience, from psychology to flight simulators.
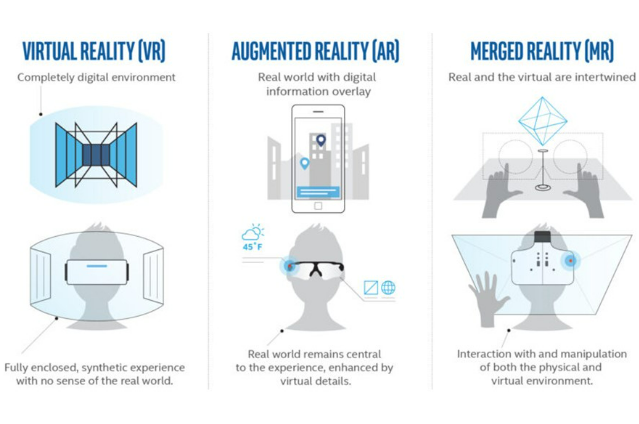
- Virtual Reality (VR):
Virtual Reality is the most popular extended reality technology at the moment (VR). It is usually understood to be an immersive, interactive computer-generated experience where the user fully experiences a virtual environment. In virtual reality, reality and the created world do not interact, nor does the user engage with both worlds at once.
There are numerous VR genres with various densities of inhabitants. While desktop VR uses computer graphics to create a synthetic, livable 3D environment with only a personal computer, the most immersive possibilities require an HMD or cave to totally separate the actual from the synthetic environment. Video mapping transforms everyday items or spaces into 3D displays, and 360-degree videos immerse a single person in a fully digital setting (whether live action or computer-generated). The most affordable and quickly produced VR 360 film is primarily used by the humanitarian sector4.
- Augmented Reality (AR):
AR has developed from VR. In AR, the user can engage in simultaneous interactions with the actual environment and artificial information, which is still an engaging experience. The user's vision of the real world is obscured by virtual images or information, and the virtual content does not interact with the real world in real time. Crisis Commons and OpenStreetMap used the first augmented reality application in 2011 in reaction to the earthquake in Haiti.
- Mixed Reality (MR):
The finest of both VR and AR is mixed reality (MR). In this platform, virtual information is rooted in the actual world and placed on top of it. Virtual visuals can also communicate with physical buildings. This is the most recent iteration of XR, also known as hybrid reality or merged reality.
The current focus of much technological advancement is on mixed reality. Whilst instances of AR and VR are simple to think of, mixed reality is more about combining those ideas, utilising all the available tools and technologies to produce even more thrilling experiences.
What makes folks matter?
As more Americans use XR tools, the market for immersive technologies is expanding quickly. Numerous uses for these products include workforce development, remote teamwork, innovative client experiences, and more immersive learning opportunities. The design of XR tools is also developing and aiding in acceptance. For example, XR headsets are getting smaller and easier to use, which is drawing in new user populations. Additionally becoming more realistic and user-friendly are the design and user experiences.
According to Statista, the VR market's revenue will increase from less than $5 billion to more than $12 billion in three years. PwC projects that by 2030, XR will have increased the U.S. GDP by up to $500 billion and the global economy by $1.5 trillion. Furthermore, PwC predicts that VR and AR technology will improve over 2 million occupations by 2030.
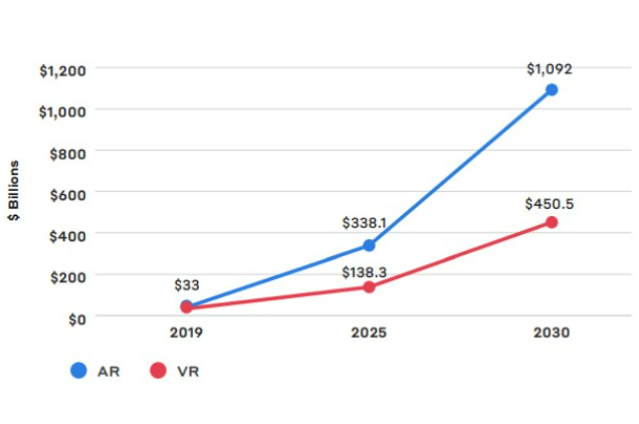
GDP contribution of VR and AR projected worldwide
The Wide focused industries
The invention of the Sword of Damocles, a head-mounted display of computer-generated visuals, led to the introduction of XR in the 1960s. The National Football League (NFL) added the yellow line that signifies a first down during live broadcasts in the late 1990s, which greatly increased the public's exposure to AR. However, analysts predict that the XR market will continue to expand over the coming years across a variety of industries, including health care, education, and real estate, despite the fact that it initially took off in the gaming and entertainment industries.
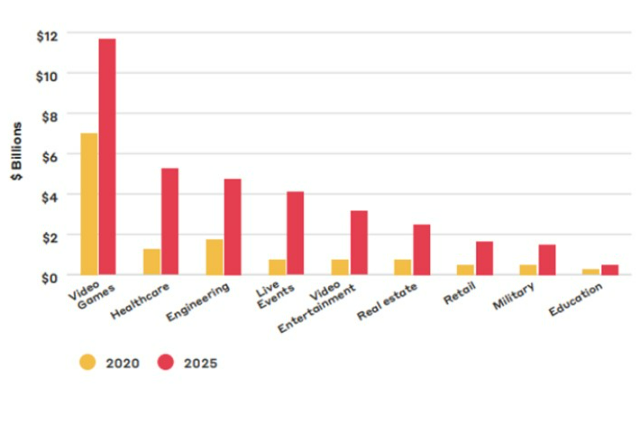
- Healthcare sector:
In the field of medicine, surgeons and physicians are receiving training in virtual reality (VR) to carry out activities in immersive environments while under extreme time pressure and stress, such as training to extract transvenous lead. Similarly, by superimposing patient information in their field of vision during a procedure, physicians can employ AR to free up their hands. For instance, the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and Medivis, an FDA-approved AR surgical system used in the operating theatre to assist surgeons with challenging tasks, collaborated to enhance medical solutions for those who served.
- Live events and trainings:
Immersive technologies offer substitutes for some in-person workforce trainings that might be too risky, expensive, or difficult to carry out in the real world. One estimate states that by 2030, XR tools might increase workforce training and development by about $300 billion. 9 XR technologies can be used in a range of training contexts, including military simulations, professional sports, and public speaking. To help EMTs prepare for harsh real-world occurrences through simulation, Austin, Texas, for instance, invested in VR training programs. Similar public-private partnerships are growing in number to fund immersive training opportunities.
- Advertising and Marketing Sectors:
Other sectors are integrating immersive technologies into their advertising and marketing strategies. Customers can examine items for sizing and attractiveness using mobile AR apps that overlay virtual copies of furniture, clothing, and accessories in a user's home or on their body in the retail industry. Virtual reality (VR) is being utilised in the real estate sector to provide virtual tours of homes, giving potential buyers the chance to acquire a sense of a property without having to physically visit the location.
- Tourism Industry:
Starting to use virtual reality to transport people to locations that are too risky, remote, or unlikely for them to visit. For instance, individuals can visit the International Space Station virtually, investigate the Great Barrier Reef, or go up close to a well-known piece of art like the Mona Lisa. These experiences may become more widely available to a bigger group of people thanks to virtual reality.
Example:
Imagine visiting a city where all the tourist attractions are available in your local language via an app. where you can create installations with your smartphone, eliminating the need to wait in lines for exhibitions. Or in situations where virtual reality (VR) recreations of historical events bring heritage places to life.
Tourism is being redefined by smart cities.
Travel limitations brought on by the pandemic for two years altered how we view the world. We were able to take virtual tours from the comfort of our couches, and video calls replaced business trips. You might imagine robots navigating the streets, flying automobiles gliding through the air, or artificial intelligence running city services when you hear the term "smart city." The truth is a little different, but it's just as thrilling.
Even before the pandemic, the capital of Denmark took the lead in this. With the aid of touch screen guidance, robots, and VR goggles, the Copenhagen Visitor Service encourages visitors to plan their itineraries, and an app disseminates information and gathers data to assist the service run more smoothly.
Destinations like Paphos, Cyprus, and Zagreb, Croatia, spare no effort in their quest to join these ranks.
They are creating virtual experiences that are often exclusive to the gaming sector using technology like augmented reality (AR).
Both cities have been nominated for the 2023 European Capital of Smart Tourism, a competition that honours excellent accomplishments by European cities as travel destinations, thanks to these projects.
- Military
The US Military has poured billions of dollars on XR technologies since their inception. The Integrated Visual Augmentation System (IVAS), which mixes synthetic training environments with actual data to improve infantry readiness and effectiveness, has been purchased by the Army and the Marine Corps. Similar XR technology have been used by the Navy and Air Force to educate their jet pilots.
The US Defense Department is quick to hail the limitless potential of XR advancements for significantly better training, situational awareness, logistics support, combat preparedness, and even medical training and procedures. In many instances, XR can give training far more quickly and inexpensively than traditional training. The US Air Force has cut the length of pilot training from 12 months to 4 months by utilizing virtual reality, artificial intelligence (AI), and biometric tracking.
Using XR technologies, military personnel can train and rehearse for anticipated battle scenarios, know the location of friendly troops or reported threats, and even overlay virtual enemies and obstacles as needed for better preparation. By superimposing virtual data over a view of the real world, military personnel can navigate more easily across any terrain in the world.
What makes XR unique?
With higher efficiency and increased production, AR enhances and even redefines how employees and customers execute difficult, expensive, or even physically impossible jobs. Businesses are benefiting greatly from augmented reality in a variety of use cases:
- More accurate visualization: Use lifelike information and graphic overlays to boost productivity.
- Better communication: AR shared content and experiences, enables quicker decision-making and improves service.
- Remote mastery: Support activities carried out remotely. Cut back on shipping and trip costs.
- Enhanced service: Replace outdated procedures and give new ones life. Shorten wait times and enhance customer relations.
- Flexible training : Allows employees to receive training remotely or on-site while working more effectively.
A Big Project - Dubai Metaverse Strategy
The Dubai Crown Prince and Chairman of Dubai's Higher Committee of Future Technology Development and Digital Economy, Sheikh Hamdan bin Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, recently approved the new phase of the Dubai Metaverse Strategy to advance the digital economy and take steps to make it simpler to use the metaverse and new technologies in the future. Launched in July 2022, the Dubai Metaverse.
What is Metaverse?
Science fiction writer Neal Stephenson used the phrase "metaverse" for the first time in 1992, and video game firms frequently utilised it after that. It is the newest iteration of the Internet, one that emphasises social interaction. People can utilise their digital avatars to immerse themselves in virtual and augmented realities in the futuristic virtual world known as the Metaverse.
Through the integration of social media principles, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and blockchain, Metaverse offers venues for rich user interaction. You may think of it as a 3D virtual environment with shared characteristics that are continually changing for all of its inhabitants, a virtual world with ongoing events and an online infrastructure. Theoretically speaking, it captures everything occurring in reality and will deliver upcoming updates and happenings in real-time. In a borderless virtual environment, the user is present.
What is the purpose?

The Dubai Metaverse Strategy intends to make the Emirate one of the top ten metaverse economies in the world as well as a global centre for the metaverse community. The emphasis is on expanding on Dubai's achievement of drawing more than 1,000 blockchain and metaverse companies.
It is presented to encourage the growth of Web3 technology and its applications for new governmental work patterns and growth in important industries like tourism, education, retail, remote work, healthcare, etc. The approach also aims to create global standards for creating safe and secure platforms for users, as well as metaverse infrastructure and legislation to hasten the adoption of these technologies.
Over 40,000 virtual jobs will be created by 2030
The plan helps Dubai achieve its goal of creating over 40,000 virtual jobs by 2030. This should help the UAE government achieve its objective of doubling the number of blockchain businesses currently operating and help Dubai's economy grow even further.
Sheikh Hamdan noted during the introduction in July that the Dubai Metaverse Strategy intends to promote technological innovation. More than 1,000 blockchain and metaverse-related businesses are based in Dubai, which generates $500 million for the local economy.
What are the strategy's main pillars?
The main pillars of the strategy include extended reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), mixed reality, and digital twins (a virtual version of an object or system). By utilising real-time data, machine learning, IoT, AI simulation, and blockchain, it focuses on enhancing human thought processes.
Data, network, cloud, and edge computing are the four technological pillars of the metaverse strategy, and they are all focused on real-world data collecting, validation, storage, processing, and management. Other points of support include expanding the whole range of 5G organizations to enable edge processing and provide on-demand PC system resources. Data can be gathered, processed, and stored locally via smart devices and local networks as opposed to being sent to the cloud.
Is it the next step in the growth of social connections?
No one owns the platform, which is open. According to Facebook, the metaverse represents the next step in the growth of social connections. Many people and corporations will run their own locations in the virtual world. A mixed reality that mixes virtual and augmented reality is known as a metaverse. In the Metaverse, digital elements will be incorporated into the physical world, and it will support virtual 3-D environments.
Currently, the metaverse idea has been successfully applied across many game platforms. For instance, Epic Games' Fortnite video game recently featured a concert by Ariana Grande.
A cryptocurrency is another component of a virtual universe that has been successfully realized; it will be used in the new metaverse global order to pay for all services.
XR'S projections for the long term
- As spectators foot upon mars alongside the first astronaut around 2026, the mars landing will be a turning point for XR.
- Wills will frequently contain provisions for the ownership of virtual property, virtual money, and other metaverse assets.
- By 2030, more physical conscious time will be spent in the metaverse than in the physical world, and the financial worth of assets in the metaverse will begin to threaten that of assets in the physical world. In the metaverse, it is typical for people to apply for jobs, make a living, shop, meet friends, and even get married.
- Wafer-like glasses and contact lenses allowing spatial collaboration across multiple disciplines will take the role of the flatscreen, keyboard, and mouse by the year 2030. It will develop a new control interface.
- For shopping and other activities, as well as remote help with information overlayed in XR, digital persons will provide customer service by the year 2030.
- Robots will solve problems and protect humans from dangerous jobs by 2030 using artificial data created from a virtual reality.
- Higher education will be more widely available and provided on a virtual campus with digitised resources like museums as a service.
- By 2030, XR and brain computer interfaces (BCIS) will enable the tracking, recording, and manipulation of human mind, leading to the need for privacy-focused regulation. Instead of memorising information, brain capacity will be employed to make decisions.
- In order to promote higher interoperability and portability, XR technologies will attain horizontal convergence by 2030.
- By 2023, board meetings will take place in the metaverse. In terms of how businesses and the government communicate and work together to share information in the upcoming years, XR will be taken for granted.
A hypothetical illustration - On the future world
A small illustration on XR:
On her first day of work, a construction worker is utilizing a virtual reality (VR) training module to learn how to weld. The program guides her through each step as she picks up welding equipment to weld a metal beam in a simulated environment. She is not new to virtual reality; in fact, she had previously utilized it as a component of an exposure therapy treatment plan to help her overcome her fear of heights by exposing her to them virtually. Even though she is comfortable with VR, she is worried about the data that her employer could be gathering with the VR headset.
She had heard that the VR headset recorded information about her eye movements, which could be used to deduce private details about her physical and mental well-being. However, she is appreciative that VR is making such training more accessible and that recent improvements in broadband and 5G in her area have made it possible for such VR programs. She worries that the regional imbalances were made worse by the fact that her town's broadband expansion occurred later than others in the area. The construction worker is given a set of augmented reality (AR) glasses after her training session. They add virtual labels over the boxes that she must move around the construction site, so she is eager to use them.
She is unsure of the privacy protections in place, though, and worries that her glasses could record private information about passersby passing the construction site on their way into a nearby medical facility. Using the GPS on her AR glasses, the construction worker navigates on her way home from work. She hears a legislator discussing whether industry has established the proper standards for immersive technology and whether lawmakers should step in with new legislation and regulation on a local radio station. Her adolescent son uses virtual reality to interact with his pals, but she is unsure if the parental safeguards she set up are sufficient to shield him from inappropriate material. The construction worker ponders her experiences with immersive technologies as the politician wraps up his speech and wonders if the industry and legislators had been designing, implementing, and developing policy around VR and AR tools with individuals like her in mind.
The hypothetical narrative above demonstrates how common people might be impacted by immersive technology, including VR and AR, as well as some of the potential and challenges they provide. Immersive technologies are becoming more and more popular, and 5 people are using them for a variety of things, like manufacturing, retail, and health care. Society needs to consider the ramifications carefully. The development and application of these technologies can be significantly influenced by industry standards and governmental regulation.
Challenges
- Cost - Depending on the intricacy of the object and whether it contains additional digital assets like CAD files, the cost to capture a single object can range from $1,000 to $35,000. Dimensionally precise 3D models and environments that can be immediately experienced in VR and compatible devices, like the Oculus, can take months to develop and create.
- Time to development - In the Unity3D engine, a 5,000 square foot virtual world may be created in six to twelve weeks. That can be a lot to ask when designing a pilot programme for businesses that are just starting to investigate the advantages of XR.
- User Experience - This is a major problem. Poor UX was cited as the biggest obstacle to both AR and VR adoption in a Perkins Coie poll for the past two years. This may seem as troubles engaging with 3D objects, problems navigating photorealistic surroundings, or problems understanding how to use menus, controls, etc. Human centred design (HCD), a creative method that stresses giving the user journey first priority, must be the foundation of UX for XR content.
- Other include:
- Distraction brought on by uncomfortable headsets
- A lack of experience navigating virtual environments
- Misalignments between the assessment procedure and the content being evaluated.
Conclusion:
The concept of XR is entertaining and looks to be made for gaming and amusement, but it is actually ideal for internet marketing and business. Extended reality has the potential to alter how we connect with our brands, consumers, team, and the rest of the world, from product creation to customer service.
There are numerous reasons to think extended reality will play a role in how the corporate sector develops in the future.
“Identity within the XR is a very complex topic, because the way we interact and the embodiment within the metaverse provides possibilities to remain anonymous, share one’s own identity, or create an entirely new one.” - Unasoftic, Co-Founder Intertangible
. . .
References:
- https://www.xcubelabs.com/blog
- https://overlyapp.com/blog/
- https://www.business-standard.com/
- https://www.businesswire.com/news/
- https://www.marketscreener.com/
- https://www.interaction-design.org/