"Cybersecurity is one of the greatest challenges we face in the digital age." - Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
As per the quote, in the ever-evolving landscape of technology, each passing year witnesses remarkable advancements. Yet, alongside this progress, the specter of cybersecurity threats looms large, with hacking incidents proliferating and breaching barriers becoming increasingly prevalent. This dynamic environment underscores the pressing need for heightened vigilance and innovative solutions to safeguard our digital realm.
In our interconnected digital world, the threat of software supply chain attacks looms large. These attacks, which involve embedding malicious code into trusted software, can have devastating consequences for organizations and individuals alike. Recently, the cybersecurity community was jolted by the discovery of a backdoor in XZ Utils, a widely-used compression utility integrated into many Linux distributions. This backdoor, hidden in an experimental version of the software, posed a serious security risk, potentially allowing hackers to gain unauthorized access to systems. The incident underscores the pressing need for heightened security measures and proactive measures to defend against emerging threats in the software supply chain."
INTRODUCTION
XZ UTILS
XZ Utils, a no-cost utility for file compression on Linux and related systems, is highly valued for its ability to significantly reduce file sizes while preserving crucial data. Renowned for its exceptional proficiency in lossless data compression, XZ Utils excels in reducing the size of files without compromising the integrity or quality of the data contained within them. The significance of XZ Utils lies in its unparalleled ability to efficiently compress and decompress data while preserving its integrity, rendering it indispensable across a diverse spectrum of applications and use cases within the Unix-like ecosystem. Key features include:
- Efficient Compression: XZ Utils excels at file reduction, often achieving reductions of 30-50% compared to alternatives like gzip or bzip2.
- File Formats: Utilizing .xz and .lzma formats, with .xz being predominant due to its versatility in compression levels.
- Speedy Processing: Opening and manipulating .xz files is swift and convenient.
- User-Friendly Commands: XZ Utils offers straightforward commands such as xz for compression, unxz for decompression, and xzcat for viewing compressed files without alteration.
- Ubiquitous Adoption: XZ Utils is integral to numerous major projects and widely utilized by Linux distributions like Fedora and CentOS.
A. Historical Background
- Roots in Community Needs: The genesis of XZ Utils can be traced back to the exigent demand within the Unix and Linux communities for efficient data compression tools capable of handling diverse workloads and datasets.
- Evolution from Predecessors: Building upon the legacy of its predecessors such as LZMA Utils, XZ Utils emerged as a robust and sophisticated solution tailored to address the evolving requirements and challenges of data compression in Unix-like environments.
- Gradual Adoption and Integration: Over the course of its development, XZ Utils witnessed a gradual but steady ascent in adoption and integration into various Unix-like operating systems and distributions. Its proven reliability, efficiency, and versatility contributed to its widespread acceptance and integration as a standard component of the Unix-like software stack.
B. Functionality and Applications
- Lossless Data Compression: At its core, XZ Utils excels in lossless data compression, employing sophisticated algorithms to reduce file sizes without compromising data fidelity. This functionality is instrumental in conserving storage space, optimizing bandwidth utilization, and expediting data transmission across networks.
- Versatility Across Unix-like Systems: XZ Utils exhibits remarkable versatility, seamlessly integrating into diverse Unix-like operating systems beyond Linux, including BSD variants and macOS. Its cross-platform compatibility underscores its utility across a broad spectrum of computing environments, from servers and workstations to embedded systems and mobile devices.
C. Importance in Software Distribution
- Packaging and Distribution: Within the realm of software distribution, XZ Utils plays a pivotal role in packaging and compressing software bundles for dissemination. By compressing software packages into smaller archives, XZ Utils facilitates faster downloads, reduces bandwidth consumption, and simplifies the deployment of software across distributed systems.
- Compatibility and Interoperability: XZ Utils' compatibility with a myriad of file formats, including TAR, ZIP, and RPM, enhances its interoperability with existing software ecosystems. This interoperability ensures seamless integration with package management systems, version control tools, and software repositories, streamlining the software development lifecycle.
D. Integration with Linux Distributions
- Inclusion in Default Installations: Many Linux distributions incorporate XZ Utils as a standard component of their default installations, underscoring its integral role in the Linux ecosystem. From Ubuntu and Debian to Fedora and CentOS, XZ Utils forms an indispensable part of the foundational software stack, empowering users with efficient data compression capabilities out of the box.
- Support for Legacy Formats: In addition to its support for the XZ compression format, XZ Utils boasts compatibility with legacy compression formats like .lzma. This backward compatibility ensures continuity for users migrating from older systems while maintaining backward compatibility with archived data and software packages.
E. Security Implications
- Vulnerability Management: As with any critical software component, maintaining the security of XZ Utils is paramount to mitigating potential risks associated with malicious exploitation or backdoor insertion. Timely identification and remediation of security vulnerabilities are essential to safeguarding system integrity and data confidentiality within Linux environments.
- Impact of Security Flaws: Security vulnerabilities within XZ Utils can have far-reaching implications, ranging from data exposure and unauthorized access to system compromise and exploitation. The exploitation of such vulnerabilities could potentially lead to widespread disruptions, data breaches, and compromise of critical infrastructure, necessitating proactive security measures and vigilant monitoring.
F. Community and Development
- Open Source Collaboration: The development of XZ Utils epitomizes the collaborative ethos of the open-source community, with contributions from developers and enthusiasts worldwide. Community-driven development ensures transparency, fosters innovation, and promotes peer review, thereby enhancing the reliability and security of XZ Utils over time.
- Versioning and Updates: The evolution of XZ Utils is characterized by iterative improvements, version updates, and the integration of security patches and bug fixes. Maintainers play a pivotal role in curating and managing these updates, ensuring the continued robustness and resilience of XZ Utils in the face of evolving threats and user requirements.
Expected behavior: Users expect XZ Utils to adhere to established norms of reliability and security. Traditionally, it operates as a trustworthy tool, safeguarding data integrity during compression and decompression processes. Its expected behavior encompasses transparent operations, free from any clandestine activities that could compromise system security.
G. Future Directions and Challenges
- Enhancements and Innovations: Looking ahead, the future of XZ Utils holds promise for further enhancements and innovations in data compression technology. Advancements in algorithms, optimizations, and parallel processing techniques may unlock new avenues for improving compression ratios, reducing processing overhead, and enhancing overall performance.
- Security Challenges: Despite its robustness, XZ Utils faces ongoing security challenges in an ever-evolving threat landscape. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort to fortify code integrity, bolster vulnerability management practices, and foster a culture of security awareness and collaboration within the XZ Utils community. Proactive measures to preemptively identify and mitigate potential security risks will be essential in safeguarding the integrity and trustworthiness of XZ Utils for years to come.
BACKDOORS: A HIDDEN THREAT IN SOFTWARE
In the intricate landscape of cybersecurity, backdoors emerge as covert pathways within software systems, circumventing standard security protocols and granting unauthorized access. They represent a formidable threat, providing a surreptitious means for nefarious actors to penetrate systems, compromise data integrity, and unleash chaos. The covert nature of backdoors renders them particularly pernicious, as they can operate stealthily, evading detection mechanisms and remaining undetected for prolonged periods.
A. Dangers Lurking within Backdoors
The presence of backdoors introduces a myriad of risks to both software integrity and system security. While the most immediate danger lies in unauthorized access, the ramifications extend far beyond mere infiltration. Backdoors serve as gateways for potential data breaches, enabling malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities and access sensitive information. Moreover, they can manipulate system functionalities, altering processes and settings to serve malicious purposes. In some cases, backdoors may even function as conduits for cyber espionage or sabotage, allowing adversaries to inflict widespread harm on targeted systems or networks. These risks transcend individual systems, posing systemic threats that can impact entire organizations or even national security infrastructure in certain scenarios.
B. Legal and Ethical Considerations
1. Legality of Backdoor Deployment
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to local regulations and international laws governing software development and cybersecurity practices. This includes regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Navigating the ethical implications of intentionally embedding backdoors into software systems. This involves considering the potential harm to individuals' privacy and security, as well as the broader societal implications of facilitating unauthorized access to digital assets.
2. Privacy and Surveillance Concerns
- Security vs. Privacy: Striking a delicate balance between the need for robust cybersecurity measures and the protection of individual privacy rights. This entails weighing the benefits of enhanced security against the potential erosion of privacy and civil liberties.
- Safeguarding Against Abuses: Implementing safeguards and oversight mechanisms to prevent the misuse of backdoors for unauthorized surveillance or data collection. This may include transparency measures, accountability frameworks, and independent audits to ensure compliance with privacy regulations and ethical standards.
SHOCKING REVELATION: UNVEILING THE XZ UTILS BACKDOOR
On March 29, 2024, the cybersecurity and open source software community was jolted by the revelation that a recent experimental version of XZ Utils, a crucial compression utility deeply embedded in numerous popular Linux distributions, contained a covert backdoor. This backdoor, if successfully exploited, would have granted unauthorized access to any system running the affected versions of XZ Utils, enabling hackers with possession of a specific private key to enter compromised systems and execute commands with elevated privileges.
A. Scrutiny and Discovery:
Recent scrutiny and examination of XZ Utils versions 5.6.0 and 5.6.1 by cybersecurity experts revealed the presence of subtle yet significant alterations in the codebase, hinting at the existence of a maliciously inserted backdoor. Through meticulous analysis and forensic investigation, cybersecurity professionals uncovered anomalous code patterns indicative of clandestine intent. This discovery shed light on the sinister nature of the backdoor, prompting immediate action within the Linux community to address the looming threat to system security.
The method used to implant the XZ Backdoor was stealthy and intricate, particularly in exploiting SSH functionality:
The hackers manipulated the liblzma library, integral to SSH operations on Linux systems, allowing them to issue commands to the SSH server clandestinely, without altering any files. Their strategy involved inserting malicious code that monitored a specific secret key during SSH logins. Upon detecting this key, the code executed commands with equivalent authority to the SSH service, granting attackers remote server control merely by utilizing the secret key. By targeting the liblzma library utilized by SSH, they evaded direct alterations to SSH-related components, effectively concealing their backdoor.
The implementation of the backdoor was notably covert:
- The hackers obfuscated the code and employed evasion techniques to evade detection by conventional scrutiny tools.
- They ensured that the backdoor's functionality remained indiscernible from normal operations to avoid raising suspicion.
- The backdoor was engineered to operate selectively, activating only under specific conditions, such as on particular Linux systems and during the creation of specific file types. This tailored approach minimized detection during routine usage.
- Furthermore, they devised a mechanism to incorporate additional covert functionalities in the future without leaving traces. These tactics collectively rendered the backdoor exceedingly challenging to uncover, akin to searching for a needle in a haystack, albeit with added complexity as the needle was disguised within the hay.
B. Shockwaves in the Linux Community:
The disclosure of the backdoor within XZ Utils sent shockwaves rippling through the Linux community, igniting concerns about the integrity and trustworthiness of widely-used software components. The realization that a fundamental tool like XZ Utils, relied upon by countless Linux users and integrated into numerous distributions, could harbor such a covert vulnerability sparked widespread alarm and raised urgent questions about the efficacy of security protocols and measures in safeguarding against sophisticated threats.
C. Implications for Linux distributions
The discovery of the backdoor has profound implications for Linux distributions, reverberating across the software supply chain. Major distributions, including Red Hat, Debian, and Fedora, now face the daunting task of assessing the extent of infiltration and mitigating potential risks. The fallout from this revelation underscores the vulnerability of software ecosystems to covert attacks, prompting a reevaluation of security protocols and response strategies.
D. Analysis of individuals involved
Forensic analysis and collaborative intelligence efforts are underway to unmask the individuals behind the backdoor. Investigators are scrutinizing the identities and motives of the actors implicated in this nefarious scheme, seeking to trace the origins of the malicious code and ascertain the extent of their involvement.
E. Motives and methods speculation
Speculation abounds regarding the motives driving the perpetrators to introduce the backdoor into XZ Utils. Potential incentives range from financial gain and corporate espionage to ideological agendas or state-sponsored cyber warfare. Concurrently, conjecture surrounds the sophisticated methods employed to orchestrate this covert operation, highlighting the need for enhanced vigilance and preemptive security measures in an ever-evolving cyber threat landscape.
F. A Chance Discovery:
The discovery of this insidious backdoor was no stroke of luck but rather the result of meticulous detective work conducted by a lone Microsoft engineer, Andres Freund. Freund's attention was drawn to anomalies within the remote connection protocol SSH while troubleshooting performance issues within a version of the Debian Linux variant. It was this keen observation and subsequent investigation that ultimately thwarted the covert infiltration before it could proliferate across countless systems worldwide.
G. Implications and Fallout:
The revelation of the XZ Utils backdoor sent shockwaves throughout the cybersecurity and open source software spheres, highlighting the inherent vulnerabilities lurking within critical components of digital infrastructure. Had it not been for Freund's vigilance and swift intervention, the consequences of this backdoor's proliferation could have been catastrophic, potentially compromising the security and integrity of millions of systems globally.
THE REVELATION
A. Andres Freund's Discovery:
Andres Freund's pivotal role in uncovering the backdoor within XZ Utils exemplifies the importance of keen observation and relentless investigation in cybersecurity. While engrossed in the intricate task of troubleshooting performance issues within Debian systems, Freund stumbled upon anomalous patterns in SSH logins. Recognizing the significance of these deviations, Freund embarked on a journey of meticulous examination to unearth the root cause.
B. Details of Uncovering the Backdoor:
Freund's investigative prowess led him to scrutinize the inner workings of XZ Utils versions 5.6.0 and 5.6.1 with unwavering precision. His thorough analysis revealed subtle but discernible alterations in the codebase, hinting at the presence of nefarious elements. These clandestine modifications, carefully woven into the fabric of the utility, raised immediate concerns regarding the integrity of Linux distributions incorporating the compromised versions. Freund's dedication to unraveling the truth laid bare the insidious nature of the backdoor, prompting swift action to address the looming security threat.
C. Initial Observations and Implications:
The discovery of the backdoor reverberated across the Linux community, serving as a stark reminder of the ever-present risks lurking within software ecosystems. Freund's astute observations shed light on the vulnerabilities inherent in widely-deployed software components, emphasizing the critical need for rigorous code review processes and proactive security measures. The implications of this revelation extended far beyond technical intricacies, highlighting the imperative of maintaining trust and integrity within open-source software communities.
D. Distribution Impact:
An analysis of the dissemination of the compromised XZ Utils versions underscored the diverse impact felt across Linux distributions. Prompt action by affected distributions mitigated the potential fallout from the security threat, demonstrating the resilience and agility of the open-source ecosystem. Through coordinated advisories and proactive measures, Linux distributions rallied to safeguard their users against the perils of the backdoor. This collaborative response exemplified the strength of community-driven efforts in fortifying defenses against emerging cybersecurity challenges.
THE MODUS OPERANDI
A. Analysis of Code Alterations:
Scrutinizing the code alterations in XZ Utils versions 5.6.0 and 5.6.1 reveals subtle yet impactful changes. These alterations, carefully embedded within the codebase, exploit vulnerabilities and introduce backdoor functionality. The attackers employed sophisticated techniques to obfuscate their modifications, making detection challenging.
B. Examination of Injection Methods:
The injection of malicious code into XZ Utils involved several intricate methods. Through analysis, it was determined that the attackers leveraged a multi-stage process, including the introduction of obfuscated scripts and the manipulation of build-time artifacts. These methods enabled the covert insertion of the backdoor without triggering immediate suspicion.
C. Targeting SSHD:
The backdoor specifically targeted the SSHD binary, a critical component responsible for SSH authentication. By compromising this binary, the attackers gained a foothold within the authentication process, allowing them to intercept and manipulate authentication requests. This strategic targeting aimed to exploit SSH connections, a commonly used method for remote access.
- Insight into Interference with SSHD: The interference with the SSHD binary involved subtle manipulations designed to evade detection. The backdoor injected malicious code into key components of the authentication process, including user verification and session establishment. This interference occurred at a critical juncture, enabling the attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems.
- Understanding Implications for SSH Connections: Compromised SSH connections resulting from the backdoor pose significant security risks. By subverting SSH authentication, the attackers could establish unauthorized access to systems, potentially compromising sensitive data and system integrity. The implications extend beyond individual systems to encompass broader network security concerns, highlighting the urgent need for remediation measures.
Who Done This?
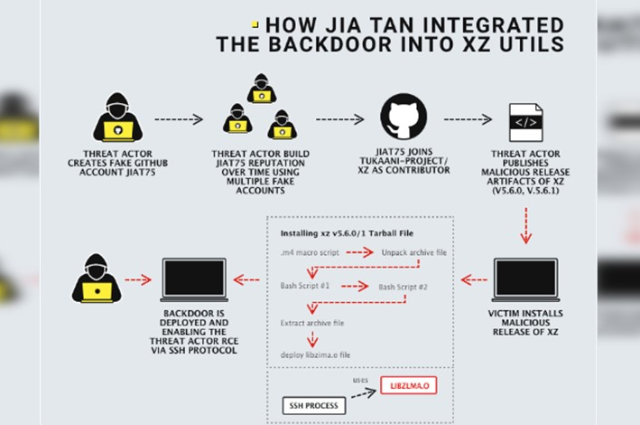
The discovery of the XZ Utils backdoor revealed that it was inserted by the main overseer of XZ Utils, known as Jia Tan. Following this revelation, questions emerged in the tech community about Jia Tan's identity and affiliations. Jia Tan took advantage of the collaborative nature of open source software development, where contributions are suggested on platforms like GitHub and reviewed by peers before integration. Reviewing Jia Tan's history in the open source realm showed their initial appearance in November 2021 under the GitHub handle JiaT75. They later contributed to various projects under the aliases Jia Tan or Jia Cheong Tan for over a year before initiating changes in XZ Utils.
A. The Enigma of Jia Tan:
Jia Tan purportedly hails from California, yet investigations into their activities suggested potential origins in Eastern Europe or Russia. Despite efforts to unveil their true identity, Jia Tan's background remains shrouded in mystery, raising questions about potential affiliations with larger entities, possibly governmental. Further investigation is warranted to unravel the complete narrative. Presently, Jia Tan's actions underscore the vulnerability of open projects to manipulation, serving as a cautionary tale regarding the allocation of trust in critical endeavors.
B. A Prolonged Scheme:
Over a span of two years, individuals claiming to be Jia Tan expressed dissatisfaction with the pace of XZ Utils updates, urging the main developer to grant them privileged access for project modifications. Upon obtaining this access, Jia Tan enacted numerous routine alterations to foster an appearance of trustworthiness. However, these actions appear to have been part of a larger strategy to surreptitiously introduce harmful code unnoticed.
C. Chronology of Events
- Initial Compromise: In the early stages of 2021, an individual operating under the pseudonym "Jia Tan" initiated preparations for an assault on XZ Utils. This entailed the creation of fictitious online identities and active engagement within the XZ Utils community, thereby cultivating an aura of credibility. By early 2023, these efforts culminated in Jia Tan attaining the authority to enact modifications within XZ Utils.
- Acquisition of Commit Access: By January 2023, Jia Tan had demonstrated their capability to contribute through minor, benign alterations. This earned them the trust necessary to undertake more significant modifications directly within XZ Utils. Throughout this period, Jia Tan maintained a facade of helpfulness while covertly devising plans to introduce detrimental code.
- Integration of the Backdoor: Between February and March 2024, Jia Tan surreptitiously injected hazardous code into versions 5.6.0 to 5.6.1 of XZ Utils. This code was meticulously concealed to evade detection by automated scrutiny mechanisms. Its purpose was to empower attackers with clandestine control over segments of the system utilizing XZ Utils for secure connections.
- Discovery and Public Disclosure: On April 1, 2024, anomalies in XZ Utils' behavior concerning secure connections were noted by Andres Freund. Subsequent examination revealed the presence of concealed malicious code that had evaded detection for over a year. Upon thorough verification, Freund shared this discovery on April 4, prompting urgent alerts and extensive inspection and remediation efforts by concerned individuals committed to upholding system security.
D. Speculation and Concealment
Jia Tan's meticulous approach, coupled with the technical intricacy of the backdoor itself, led many cybersecurity experts to speculate that Jia Tan could be a pseudonym for a state-sponsored hacking group. Costin Raiu, a former senior researcher at Kaspersky, suggested that the operation bore the hallmarks of a sophisticated, long-term infiltration effort, potentially orchestrated by nations like China, Russia, or North Korea.
E. Concealment Measures
As scrutiny intensified following the exposure of the XZ Utils backdoor, researchers observed that Jia Tan had taken extensive measures to conceal their identity. They maintained a remarkably low online profile, with no discernible trace beyond their contributions to open source projects. Communication was routed through a VPN with a Singaporean IP address, further complicating efforts to identify them.
F. Trust and Deception
Despite the covert nature of their activities, Jia Tan's extensive contributions to the open source community provided a veneer of credibility, fostering trust among fellow developers. However, subsequent analysis revealed potentially malicious alterations to key components like the "libarchive" compression library, hinting at ulterior motives beneath the façade of collaboration.
G. Speculation and Attribution
The technical sophistication of the backdoor, coupled with discrepancies in commit timestamps, prompted speculation about the origins of the operation. While initial indicators pointed towards East Asia, further investigation suggested manipulation of commit timestamps, casting doubt on geographical attributions. Nonetheless, security experts pointed to groups like Russia's APT29, known for their expertise in supply chain attacks, as potential culprits.
H. Impact and Response
- Limited Real-World Impact: Despite the potential catastrophic implications of the discovered backdoor, its real-world impact was fortunately limited. The early detection and intervention by vigilant individuals within the cybersecurity community played a pivotal role in mitigating the threat before widespread exploitation could occur. While the discovery sent shockwaves through the tech world, swift action by Linux distributions and package managers averted the worst-case scenario.
- Addressing the Threat: In response to the identified security threat, Linux distributions and package managers swiftly mobilized to implement comprehensive measures aimed at neutralizing the risk posed by the compromised versions of XZ Utils. These measures encompassed a multifaceted approach, including:
- Issuing Advisories: Linux distributions promptly disseminated advisories alerting users to the presence of the backdoor and providing guidance on mitigating the associated risks. These advisories served as crucial communication channels for informing users about the security threat and recommended actions to safeguard their systems.
- Removal or Patching of Affected Versions: To prevent further exposure to the backdoor, Linux distributions and package managers took immediate steps to remove or patch the compromised versions of XZ Utils. This proactive approach involved replacing the tainted software with clean, secure alternatives or applying patches to rectify the vulnerabilities exploited by the attackers.
- Enhancing Security Protocols: Recognizing the need to fortify defenses against similar supply chain attacks in the future, Linux distributions and package managers initiated efforts to enhance security protocols. These initiatives encompassed rigorous code review processes, stricter verification mechanisms, and heightened vigilance to detect and respond to potential threats promptly.
By swiftly addressing the identified security threat and implementing robust mitigation measures, Linux distributions and package managers demonstrated their commitment to safeguarding the integrity and security of the open-source software ecosystem. The coordinated response underscored the importance of proactive cybersecurity practices and collaborative efforts in mitigating supply chain risks and preserving trust in critical software components.
I. Analysis of the Backdoor
1. Functionality and Consequences:
Upon dissecting the injected code, security experts discerned its operational functionality and potential repercussions for system security. The backdoor, ingeniously crafted to exploit vulnerabilities in XZ Utils, posed multifaceted risks to affected systems. Its primary functionality involved intercepting SSH authentication processes, enabling unauthorized access to compromised systems. By injecting malicious code at a critical juncture in the login process, the backdoor circumvented conventional security measures, granting adversaries elevated privileges within the system.
Technical Insights:
- The injected code leveraged sophisticated techniques to obfuscate its presence and evade detection by conventional security tools.
- Analysis of the code revealed intricate algorithms designed to intercept SSH authentication requests and manipulate data transmission to facilitate unauthorized access.
- Security researchers identified distinct patterns indicative of malicious intent, including anomalous system behaviors and deviations from expected protocol standards.
- Through reverse engineering and code analysis, researchers gained insights into the backdoor's inner workings, unraveling its mechanisms for exploiting vulnerabilities within XZ Utils.
MORALE
A. Lessons Learned
1. Significance of Timely Detection:
The incident underscored the critical importance of early detection in mitigating supply chain attacks and minimizing their impact on affected systems. The swift identification of the backdoor by vigilant developers and security researchers prevented widespread exploitation and averted potentially catastrophic consequences. Timely intervention mechanisms, such as anomaly detection algorithms and continuous monitoring protocols, played a pivotal role in curtailing the threat posed by the backdoor.
2. Transparency and Trustworthiness:
The incident underscored the indispensable role of transparency and accountability in ensuring the trustworthiness of open-source software projects. Heightened transparency measures, including rigorous code review processes and comprehensive documentation practices, are essential for fostering trust among users and stakeholders. By adhering to stringent quality assurance standards and promoting transparency throughout the software development lifecycle, open-source communities can uphold the integrity of their projects and mitigate the risk of supply chain attacks.
B. Recommendations
Proactive Security Measures:
To fortify software security and resilience against supply chain attacks, Linux users and distributors are encouraged to implement proactive security measures. These measures encompass a spectrum of strategies, including:
- Enhanced code review processes to detect and remediate vulnerabilities in software components.
- Adoption of robust verification mechanisms, such as digital signatures and cryptographic hashes, to validate the integrity of software packages.
- Implementation of secure development practices, including secure coding standards and vulnerability management protocols, to mitigate risks throughout the software development lifecycle.
The discovery of the backdoor in XZ Utils underscores the urgent need for collective action to fortify security practices and uphold trust within open-source software ecosystems. This incident serves as a wake-up call, highlighting the vulnerabilities inherent in software supply chains and the critical importance of proactive defense mechanisms.
- Strengthening Security Practices: First and foremost, the Linux community must prioritize the enhancement of security practices across the software development lifecycle. This entails implementing robust measures to identify, mitigate, and prevent security vulnerabilities at every stage of the process. From stringent code review processes to comprehensive vulnerability management protocols, proactive security measures are essential for safeguarding against emerging threats.
- Preserving Trust and Integrity: Maintaining trust and integrity within open-source software ecosystems is paramount. Transparency, accountability, and integrity must be upheld as foundational principles guiding software development practices. By fostering a culture of transparency and accountability, open-source communities can instill confidence among users and stakeholders, thereby preserving trust in the reliability and security of software projects.
- Embracing Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Collaboration and knowledge sharing are key pillars of resilience in the face of evolving cybersecurity threats. The Linux community must embrace a collaborative approach to cybersecurity, leveraging collective expertise and resources to address common challenges and vulnerabilities. By sharing insights, best practices, and threat intelligence, stakeholders can collectively enhance the resilience of open-source software environments and mitigate risks more effectively.
- Mitigating Risks and Enhancing Resilience: Ultimately, the goal is to mitigate risks and enhance the resilience of software environments against future threats. This requires a concerted effort to stay abreast of emerging vulnerabilities, evolving attack vectors, and best practices in cybersecurity. By proactively addressing security risks and fortifying defenses, the Linux community can better protect against potential exploits and uphold the integrity of software ecosystems.
Conclusion
"The XZ Utils incident underscores the critical importance of transparency and diligence in maintaining the security of open-source software ecosystems." - Linus Torvalds, Creator of Linux
"As stewards of open-source software, it's imperative that we remain vigilant and proactive in addressing security vulnerabilities to preserve the trust of users worldwide." - Mark Shuttleworth, Founder of Ubuntu
"The XZ Utils backdoor serves as a wake-up call for the entire open-source community, emphasizing the need for robust security measures and collaborative efforts to protect against emerging threats." - Jim Zemlin, Executive Director of the Linux Foundation
The incident involving the backdoor in XZ Utils serves as a catalyst for action, prompting the Linux community to redouble its efforts in strengthening security practices, preserving trust, and fostering collaboration. By embracing a proactive approach to cybersecurity and working together to address common challenges, stakeholders can mitigate risks, enhance resilience, and safeguard the integrity of open-source software environments for years to come.
. . .
References:
- https://www.wired.com/
- https://arstechnica.com/
- https://www.akamai.com/
- https://convertcase.net/
- https://daily.dev/
- https://www.livemint.com/
- https://abcnews.go.com/
- https://frontline.thehindu.com/
- https://www.cnbctv18.com/
- https://www.bbc.com/
- https://www.cfr.org/
- https://www.businesstoday.in/
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/
- https://www.theguardian.com/
- https://www.un.org/
- https://www.nytimes.com/
- https://www.vox.com/
- https://apnews.com/
- https://www.csis.org/
- https://ceodelhi.gov.in/
- https://awbi.in/